Input interpretation
trisilane
Chemical names and formulas
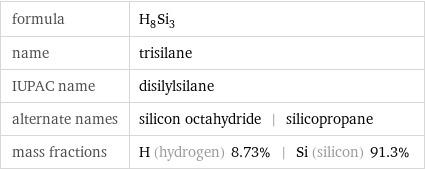
formula | H_8Si_3 name | trisilane IUPAC name | disilylsilane alternate names | silicon octahydride | silicopropane mass fractions | H (hydrogen) 8.73% | Si (silicon) 91.3%
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of trisilane. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the hydrogen (n_H, val = 1) and silicon (n_Si, val = 4) atoms: 8 n_H, val + 3 n_Si, val = 20 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for hydrogen (n_H, full = 2) and silicon (n_Si, full = 8): 8 n_H, full + 3 n_Si, full = 40 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 40 - 20 = 20 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. There are 10 bonds and hence 20 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 20 - 20 = 0 electrons left to draw and the diagram is complete: Answer: | |
3D structure

3D structure
Basic properties
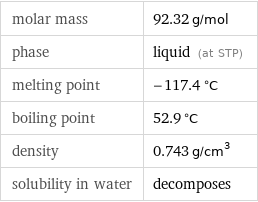
molar mass | 92.32 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) melting point | -117.4 °C boiling point | 52.9 °C density | 0.743 g/cm^3 solubility in water | decomposes
Units

Liquid properties (at STP)
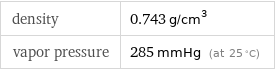
density | 0.743 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 285 mmHg (at 25 °C)
Units

Thermodynamic properties
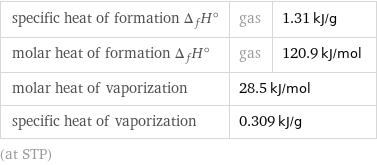
specific heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | 1.31 kJ/g molar heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | 120.9 kJ/mol molar heat of vaporization | 28.5 kJ/mol | specific heat of vaporization | 0.309 kJ/g | (at STP)
Chemical identifiers
![CAS number | 7783-26-8 PubChem CID number | 139070 SMILES identifier | [SiH3][SiH2][SiH3] InChI identifier | InChI=1/H8Si3/c1-3-2/h3H2, 1-2H3](../image_source/b78860c0cb068197b41f6989c6518f9f.png)
CAS number | 7783-26-8 PubChem CID number | 139070 SMILES identifier | [SiH3][SiH2][SiH3] InChI identifier | InChI=1/H8Si3/c1-3-2/h3H2, 1-2H3
NFPA label

NFPA label
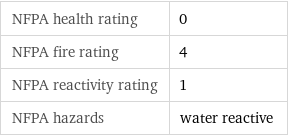
NFPA health rating | 0 NFPA fire rating | 4 NFPA reactivity rating | 1 NFPA hazards | water reactive
Safety properties

flash point | 0 °C autoignition point | 54 °C

DOT hazard class | 4.2 DOT numbers | 3194