Input interpretation
speed of sound in an ideal gas by pressure
Equation
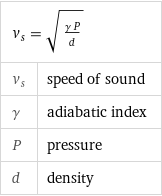
v_s = sqrt((γ P)/d) | v_s | speed of sound γ | adiabatic index P | pressure d | density
Input values

adiabatic index | 7/5 (diatomic gas) pressure | 1 atm (atmosphere) density | 1.225 kg/m^3 (kilograms per cubic meter)
Results

speed of sound | 340.3 m/s (meters per second) = 761.2 mph (miles per hour) = 1225 km/h (kilometers per hour) = 29401 km/day (kilometers per day) = 0.3403 km/s (kilometers per second)
Possible intermediate steps

Calculate the speed of sound using the following information: known variables | | γ | adiabatic index | 7/5 (diatomic gas) P | pressure | 1 atm d | density | 1.225 kg/m^3 Convert known variables into appropriate units using the following: 1 atm = 1.0133×10^8 g/(m s^2): 1 kg/m^3 = 1000 g/m^3: known variables | | γ | adiabatic index | 7/5 P | pressure | 1.0133×10^8 g/(m s^2) d | density | 1225 g/m^3 The relevant equation that relates speed of sound (v_s), adiabatic index (γ), pressure (P), and density (d) is: v_s = sqrt((γ P)/d) Substitute known variables into the equation: known variables | | γ | adiabatic index | 7/5 P | pressure | 1.0133×10^8 g/(m s^2) d | density | 1225 g/m^3 | : v_s = sqrt((7×1.0133×10^8 g/(m s^2))/(5×1225 g/m^3)) Separate the numerical part, sqrt((7×1.0133×10^8)/(5×1225)), from the unit part, sqrt((g/(m s^2))/(g/m^3)) = m/s: v_s = sqrt((7×1.0133×10^8)/(5×1225)) m/s Evaluate sqrt((7×1.0133×10^8)/(5×1225)): Answer: | | v_s = 340.3 m/s