Input interpretation

lead(II) chloride | freezing point
Result

501 °C (degrees Celsius)
Unit conversions
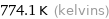
774.1 K (kelvins)

933.8 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)
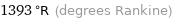
1393 °R (degrees Rankine)
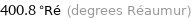
400.8 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)

270.5 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparisons as temperature
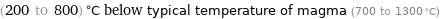
(200 to 800) °C below typical temperature of magma (700 to 1300 °C)
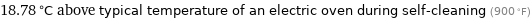
18.78 °C above typical temperature of an electric oven during self-cleaning (900 °F)
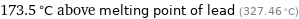
173.5 °C above melting point of lead (327.46 °C)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 67 meV (millielectronvolts)
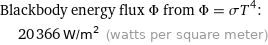
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 20366 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)
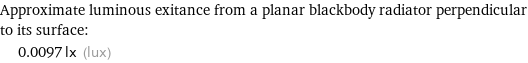
Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 0.0097 lx (lux)