Input interpretation

boiling-point elevation equation
Equation

ΔT_b = i K_b m | ΔT_b | boiling point elevation K_b | ebullioscopic constant m | solution molality i | van 't Hoff factor (assuming dilute ideal solutions)
Input values
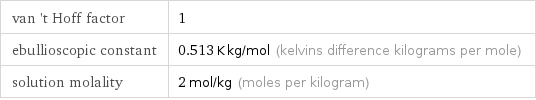
van 't Hoff factor | 1 ebullioscopic constant | 0.513 K kg/mol (kelvins difference kilograms per mole) solution molality | 2 mol/kg (moles per kilogram)
Results
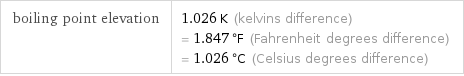
boiling point elevation | 1.026 K (kelvins difference) = 1.847 °F (Fahrenheit degrees difference) = 1.026 °C (Celsius degrees difference)
Possible intermediate steps

Calculate the boiling point elevation using the following information: known variables | | K_b | ebullioscopic constant | 0.513 K kg/mol m | solution molality | 2 mol/kg i | van 't Hoff factor | 1 Convert known variables into appropriate units using the following: 1 K kg/mol = 1000 g K/mol: 1 mol/kg = 0.001 mol/g: known variables | | K_b | ebullioscopic constant | 513 g K/mol m | solution molality | 0.002 mol/g i | van 't Hoff factor | 1 The relevant equation that relates boiling point elevation (ΔT_b), ebullioscopic constant (K_b), solution molality (m), and van 't Hoff factor (i) is: ΔT_b = i K_b m Substitute known variables into the equation: known variables | | K_b | ebullioscopic constant | 513 g K/mol m | solution molality | 0.002 mol/g i | van 't Hoff factor | 1 | : ΔT_b = 513 g K/mol×0.002 mol/g Separate the numerical part, 513×0.002, from the unit part, g K/mol×mol/g = K: ΔT_b = 513×0.002 K Evaluate 513×0.002: Answer: | | ΔT_b = 1.026 K