Input interpretation

group 12 elements | melting point
Results
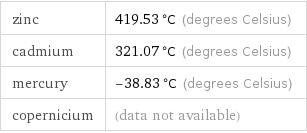
zinc | 419.53 °C (degrees Celsius) cadmium | 321.07 °C (degrees Celsius) mercury | -38.83 °C (degrees Celsius) copernicium | (data not available)
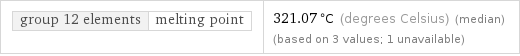
group 12 elements | melting point | 321.07 °C (degrees Celsius) (median) (based on 3 values; 1 unavailable)
Plot
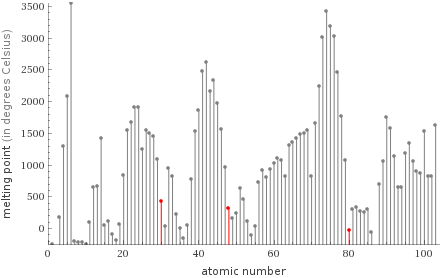
Plot
Unit conversions for median melting point 321.07 °C
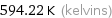
594.22 K (kelvins)

609.93 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)

1069.6 °R (degrees Rankine)

256.86 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)
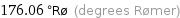
176.06 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median melting point 321.07 °C
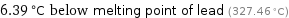
6.39 °C below melting point of lead (327.46 °C)

88.29 °C above autoignition temperature of book paper in Ray Bradbury's famous novel (451 °F)
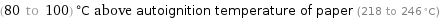
(80 to 100) °C above autoignition temperature of paper (218 to 246 °C)
Corresponding quantities
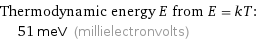
Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 51 meV (millielectronvolts)
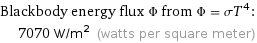
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 7070 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 1.5×10^-6 lx (lux)
Thermodynamic properties
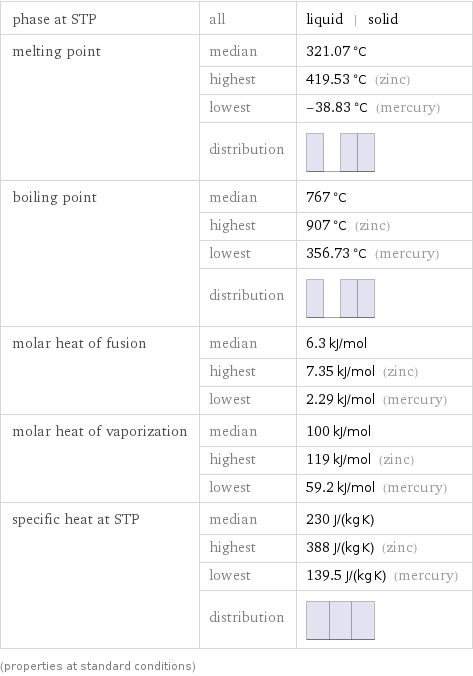
phase at STP | all | liquid | solid melting point | median | 321.07 °C | highest | 419.53 °C (zinc) | lowest | -38.83 °C (mercury) | distribution | boiling point | median | 767 °C | highest | 907 °C (zinc) | lowest | 356.73 °C (mercury) | distribution | molar heat of fusion | median | 6.3 kJ/mol | highest | 7.35 kJ/mol (zinc) | lowest | 2.29 kJ/mol (mercury) molar heat of vaporization | median | 100 kJ/mol | highest | 119 kJ/mol (zinc) | lowest | 59.2 kJ/mol (mercury) specific heat at STP | median | 230 J/(kg K) | highest | 388 J/(kg K) (zinc) | lowest | 139.5 J/(kg K) (mercury) | distribution | (properties at standard conditions)