Input interpretation
L-arginine
Chemical names and formulas
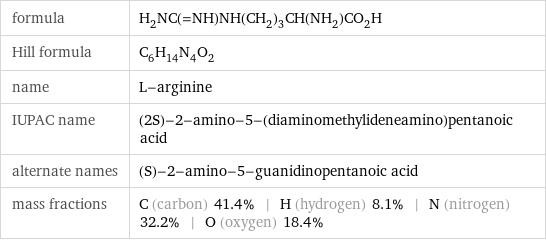
formula | H_2NC(=NH)NH(CH_2)_3CH(NH_2)CO_2H Hill formula | C_6H_14N_4O_2 name | L-arginine IUPAC name | (2S)-2-amino-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoic acid alternate names | (S)-2-amino-5-guanidinopentanoic acid mass fractions | C (carbon) 41.4% | H (hydrogen) 8.1% | N (nitrogen) 32.2% | O (oxygen) 18.4%
Lewis structure
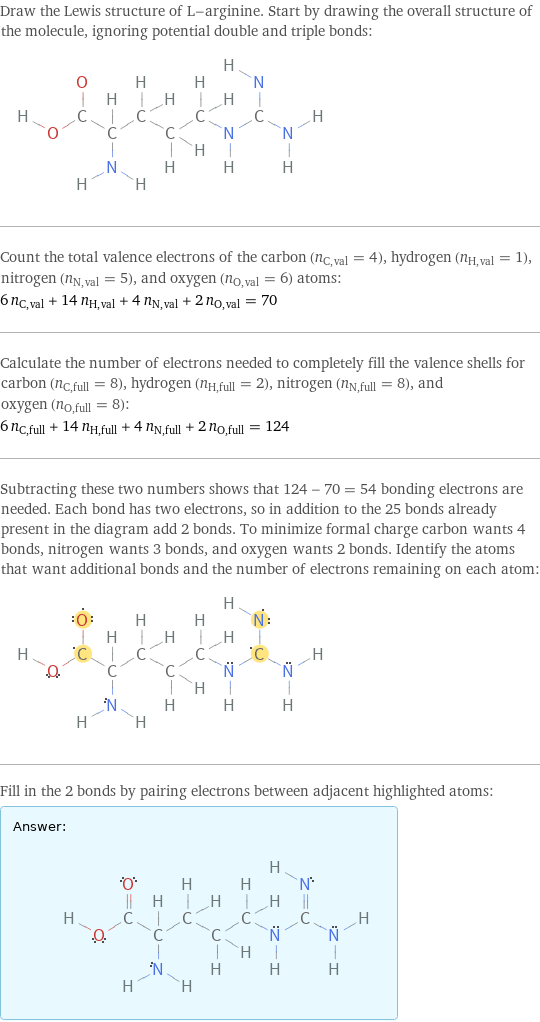
Draw the Lewis structure of L-arginine. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 6 n_C, val + 14 n_H, val + 4 n_N, val + 2 n_O, val = 70 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 6 n_C, full + 14 n_H, full + 4 n_N, full + 2 n_O, full = 124 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 124 - 70 = 54 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 25 bonds already present in the diagram add 2 bonds. To minimize formal charge carbon wants 4 bonds, nitrogen wants 3 bonds, and oxygen wants 2 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 2 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms: Answer: | |
3D structure
3D structure
Basic properties
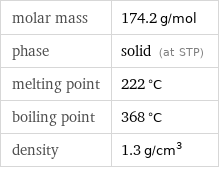
molar mass | 174.2 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 222 °C boiling point | 368 °C density | 1.3 g/cm^3
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties

experimental LogP hydrophobicity | -3.6 predicted LogP hydrophobicity | -3.86 predicted LogS | -1.36
Basic drug properties
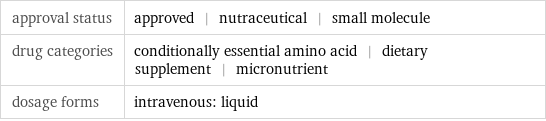
approval status | approved | nutraceutical | small molecule drug categories | conditionally essential amino acid | dietary supplement | micronutrient dosage forms | intravenous: liquid

brand names | argamine | argivene | detoxargin | levargin | minophagen A | R-gene 10 (pharmacia corp.)
Amino acid properties
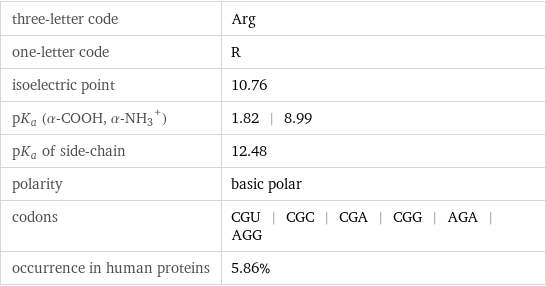
three-letter code | Arg one-letter code | R isoelectric point | 10.76 pK_a (α-COOH, (α-NH_3)^+) | 1.82 | 8.99 pK_a of side-chain | 12.48 polarity | basic polar codons | CGU | CGC | CGA | CGG | AGA | AGG occurrence in human proteins | 5.86%
Solid properties (at STP)

density | 1.3 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 2.1×10^-6 mmHg (at 25 °C)
Units

Thermodynamic properties
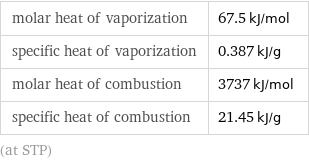
molar heat of vaporization | 67.5 kJ/mol specific heat of vaporization | 0.387 kJ/g molar heat of combustion | 3737 kJ/mol specific heat of combustion | 21.45 kJ/g (at STP)
Chemical identifiers
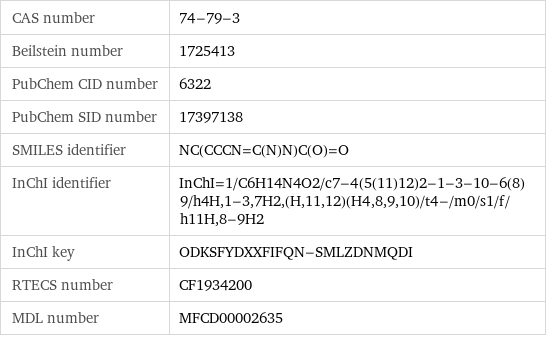
CAS number | 74-79-3 Beilstein number | 1725413 PubChem CID number | 6322 PubChem SID number | 17397138 SMILES identifier | NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(O)=O InChI identifier | InChI=1/C6H14N4O2/c7-4(5(11)12)2-1-3-10-6(8)9/h4H, 1-3, 7H2, (H, 11, 12)(H4, 8, 9, 10)/t4-/m0/s1/f/h11H, 8-9H2 InChI key | ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-SMLZDNMQDI RTECS number | CF1934200 MDL number | MFCD00002635
NFPA label

NFPA label

NFPA health rating | 1 NFPA fire rating | 0 NFPA reactivity rating | 0
Safety properties

flash point | 176 °C
Toxicity properties

RTECS classes | mutagen