Input interpretation
vitamins | melting point
Summary

median | 142 °C highest | 354 °C (pantothenic acid) lowest | 3 °C (D-alpha-tocopherol) distribution | | (based on 8 values; 3 unavailable)
Entities with missing values
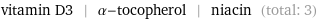
vitamin D3 | α-tocopherol | niacin (total: 3)
Melting point rankings
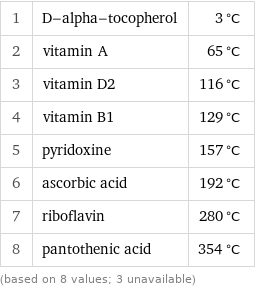
1 | D-alpha-tocopherol | 3 °C 2 | vitamin A | 65 °C 3 | vitamin D2 | 116 °C 4 | vitamin B1 | 129 °C 5 | pyridoxine | 157 °C 6 | ascorbic acid | 192 °C 7 | riboflavin | 280 °C 8 | pantothenic acid | 354 °C (based on 8 values; 3 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median melting point 142 °C
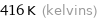
416 K (kelvins)
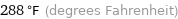
288 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)

748 °R (degrees Rankine)

114 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)
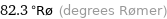
82.3 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median melting point 142 °C

(80 to 100) °C below autoignition temperature of paper (218 to 246 °C)
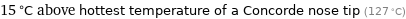
15 °C above hottest temperature of a Concorde nose tip (127 °C)
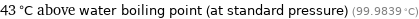
43 °C above water boiling point (at standard pressure) (99.9839 °C)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 36 meV (millielectronvolts)
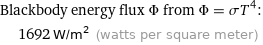
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 1692 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 2.6×10^-13 lx (lux)
Nearest corresponding gas marks for median melting point 142 °C (degrees Celsius)

| temperature | usage gas mark 1 | 140 °C | United Kingdom (actual measurements may vary)