Input interpretation

heteronuclear diatomic molecules | molar mass
Summary
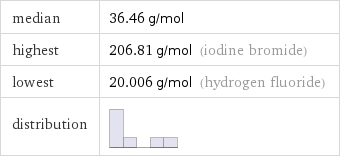
median | 36.46 g/mol highest | 206.81 g/mol (iodine bromide) lowest | 20.006 g/mol (hydrogen fluoride) distribution |
Units

Ranked values
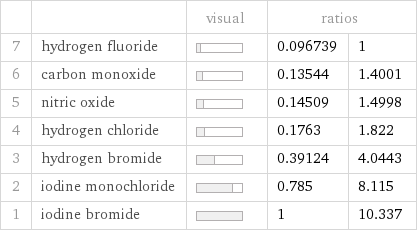
| | visual | ratios | 7 | hydrogen fluoride | | 0.096739 | 1 6 | carbon monoxide | | 0.13544 | 1.4001 5 | nitric oxide | | 0.14509 | 1.4998 4 | hydrogen chloride | | 0.1763 | 1.822 3 | hydrogen bromide | | 0.39124 | 4.0443 2 | iodine monochloride | | 0.785 | 8.115 1 | iodine bromide | | 1 | 10.337
Molar mass rankings
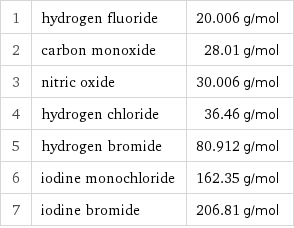
1 | hydrogen fluoride | 20.006 g/mol 2 | carbon monoxide | 28.01 g/mol 3 | nitric oxide | 30.006 g/mol 4 | hydrogen chloride | 36.46 g/mol 5 | hydrogen bromide | 80.912 g/mol 6 | iodine monochloride | 162.35 g/mol 7 | iodine bromide | 206.81 g/mol
Unit conversion for median molar mass 36.46 g/mol
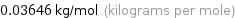
0.03646 kg/mol (kilograms per mole)
Comparisons for median molar mass 36.46 g/mol
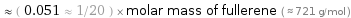
≈ ( 0.051 ≈ 1/20 ) × molar mass of fullerene ( ≈ 721 g/mol )
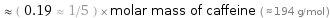
≈ ( 0.19 ≈ 1/5 ) × molar mass of caffeine ( ≈ 194 g/mol )
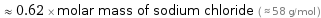
≈ 0.62 × molar mass of sodium chloride ( ≈ 58 g/mol )
Corresponding quantities
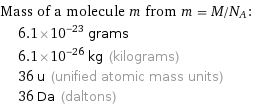
Mass of a molecule m from m = M/N_A: | 6.1×10^-23 grams | 6.1×10^-26 kg (kilograms) | 36 u (unified atomic mass units) | 36 Da (daltons)
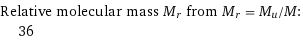
Relative molecular mass M_r from M_r = M_u/M: | 36