Input interpretation
period 4 elements | absolute boiling point
Summary
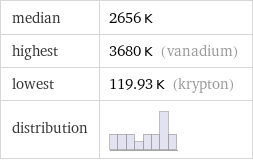
median | 2656 K highest | 3680 K (vanadium) lowest | 119.93 K (krypton) distribution |
Units

Distribution plots
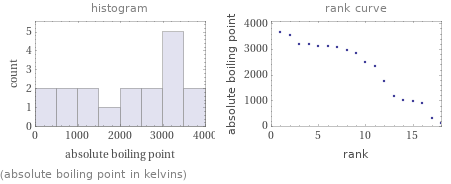
(absolute boiling point in kelvins)
Absolute boiling point rankings
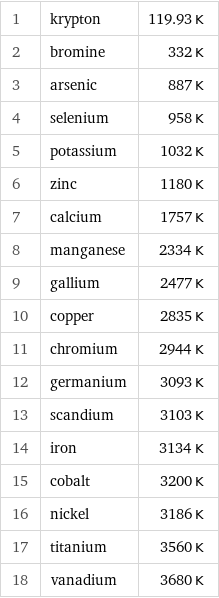
1 | krypton | 119.93 K 2 | bromine | 332 K 3 | arsenic | 887 K 4 | selenium | 958 K 5 | potassium | 1032 K 6 | zinc | 1180 K 7 | calcium | 1757 K 8 | manganese | 2334 K 9 | gallium | 2477 K 10 | copper | 2835 K 11 | chromium | 2944 K 12 | germanium | 3093 K 13 | scandium | 3103 K 14 | iron | 3134 K 15 | cobalt | 3200 K 16 | nickel | 3186 K 17 | titanium | 3560 K 18 | vanadium | 3680 K
Unit conversions for median absolute boiling point 2656 K
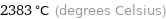
2383 °C (degrees Celsius)

4321 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)
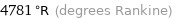
4781 °R (degrees Rankine)

1906 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)
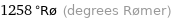
1258 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Blackbody information for median absolute boiling point 2656 K (kelvins)
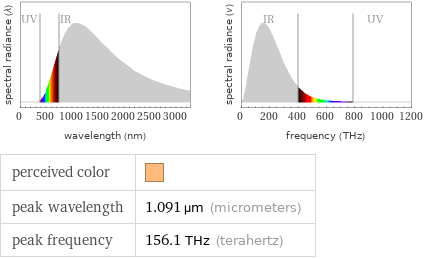
perceived color | peak wavelength | 1.091 µm (micrometers) peak frequency | 156.1 THz (terahertz)
Corresponding quantities
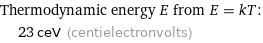
Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 23 ceV (centielectronvolts)
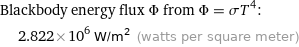
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 2.822×10^6 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 3.19×10^7 lx (lux)