Input interpretation

cerium | melting point
Result

798 °C (degrees Celsius)
Unit conversions
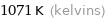
1071 K (kelvins)

1470 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)
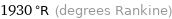
1930 °R (degrees Rankine)

638 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)
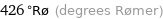
426 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparisons as temperature

502 °C below to 98 °C above typical temperature of magma (700 to 1300 °C)
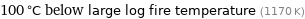
100 °C below large log fire temperature (1170 K)
Blackbody information
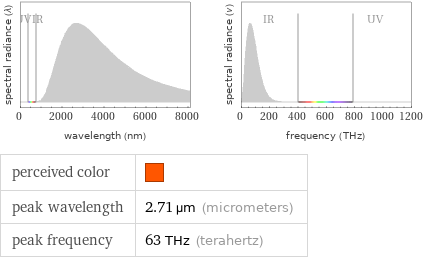
perceived color | peak wavelength | 2.71 µm (micrometers) peak frequency | 63 THz (terahertz)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 92 meV (millielectronvolts)
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 74647 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)
Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 40 lx (lux)
Thermodynamic properties
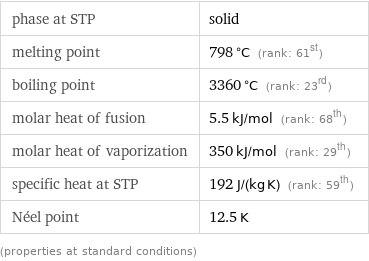
phase at STP | solid melting point | 798 °C (rank: 61st) boiling point | 3360 °C (rank: 23rd) molar heat of fusion | 5.5 kJ/mol (rank: 68th) molar heat of vaporization | 350 kJ/mol (rank: 29th) specific heat at STP | 192 J/(kg K) (rank: 59th) Néel point | 12.5 K (properties at standard conditions)