Input interpretation
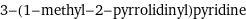
3-(1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)pyridine
Chemical names and formulas
![formula | C_5H_4NC_4H_7NCH_3 Hill formula | C_10H_14N_2 name | 3-(1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)pyridine IUPAC name | 3-[(2R)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]pyridine alternate names | 1-methyl-2-(3-pyridyl)pyrrolidine | beta-pyridyl-alpha-N-methylpyrrolidine | nicotine | pseudonicotine | pyrrolidine, 1-methyl-2-(3-pyridyl)- mass fractions | C (carbon) 74% | H (hydrogen) 8.7% | N (nitrogen) 17.3%](../image_source/f48245ffb226d9330dddcc2d3599afad.png)
formula | C_5H_4NC_4H_7NCH_3 Hill formula | C_10H_14N_2 name | 3-(1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)pyridine IUPAC name | 3-[(2R)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]pyridine alternate names | 1-methyl-2-(3-pyridyl)pyrrolidine | beta-pyridyl-alpha-N-methylpyrrolidine | nicotine | pseudonicotine | pyrrolidine, 1-methyl-2-(3-pyridyl)- mass fractions | C (carbon) 74% | H (hydrogen) 8.7% | N (nitrogen) 17.3%
Lewis structure
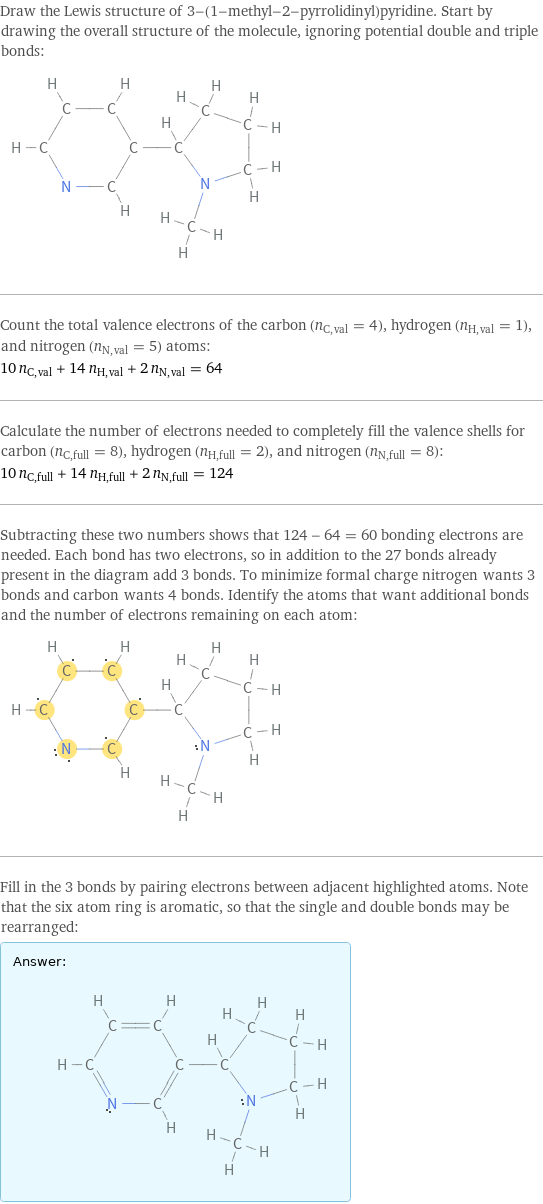
Draw the Lewis structure of 3-(1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)pyridine. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), and nitrogen (n_N, val = 5) atoms: 10 n_C, val + 14 n_H, val + 2 n_N, val = 64 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), and nitrogen (n_N, full = 8): 10 n_C, full + 14 n_H, full + 2 n_N, full = 124 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 124 - 64 = 60 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 27 bonds already present in the diagram add 3 bonds. To minimize formal charge nitrogen wants 3 bonds and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 3 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms. Note that the six atom ring is aromatic, so that the single and double bonds may be rearranged: Answer: | |
3D structure
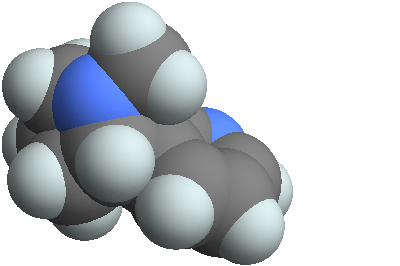
3D structure
Basic properties
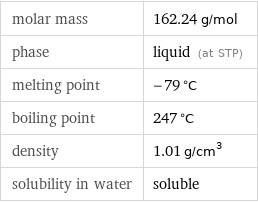
molar mass | 162.24 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) melting point | -79 °C boiling point | 247 °C density | 1.01 g/cm^3 solubility in water | soluble
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties

experimental LogP hydrophobicity | 1.1 predicted LogP hydrophobicity | 0.87 experimental LogS | 0.79 predicted LogS | -0.24 experimental Caco-2 permeability | -4.71
Basic drug properties
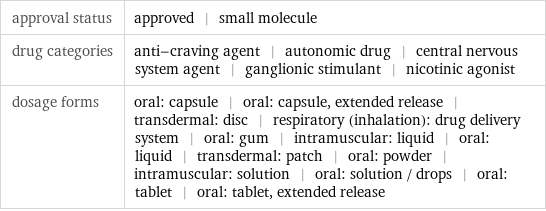
approval status | approved | small molecule drug categories | anti-craving agent | autonomic drug | central nervous system agent | ganglionic stimulant | nicotinic agonist dosage forms | oral: capsule | oral: capsule, extended release | transdermal: disc | respiratory (inhalation): drug delivery system | oral: gum | intramuscular: liquid | oral: liquid | transdermal: patch | oral: powder | intramuscular: solution | oral: solution / drops | oral: tablet | oral: tablet, extended release

brand names | black leaf | black leaf 40 | campbell's nico-soap | commit | destruxol orchid spray | emo-nik | flux maag | fumetobac | habitrol | mach-nic | niagara P.A. dust | nic-sal | nico-dust | nico-fume | nicocide | nicoderm | nicoderm Cq | nicorette | nicorette plus | nicotin | nicotina | nicotine polacrilex | nicotrol | nicotrol inhaler | nicotrol Ns | nikotin | nikotyna | ortho N-4 dust | ortho N-5 dust | prostep | tendust addiction potential of drug | 100%
Liquid properties (at STP)
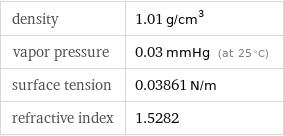
density | 1.01 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 0.03 mmHg (at 25 °C) surface tension | 0.03861 N/m refractive index | 1.5282
Units
Thermodynamic properties
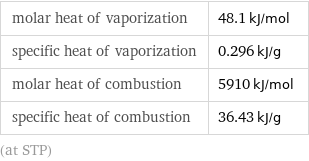
molar heat of vaporization | 48.1 kJ/mol specific heat of vaporization | 0.296 kJ/g molar heat of combustion | 5910 kJ/mol specific heat of combustion | 36.43 kJ/g (at STP)
Chemical identifiers

CAS number | 54-11-5 Beilstein number | 82109 PubChem CID number | 157672 PubChem SID number | 148704 SMILES identifier | CN1CCCC1C2=CN=CC=C2 InChI identifier | InChI=1/C10H14N2/c1-12-7-3-5-10(12)9-4-2-6-11-8-9/h2, 4, 6, 8, 10H, 3, 5, 7H2, 1H3/t10-/m1/s1 InChI key | SNICXCGAKADSCV-UHFFFAOYAX EU number | 200-193-3 RTECS number | QS5250000 NSC number | 5065
NFPA label

NFPA label

NFPA health rating | 3 NFPA fire rating | 1 NFPA reactivity rating | 0
Safety properties
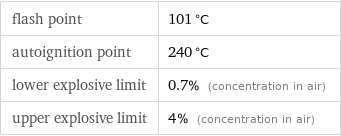
flash point | 101 °C autoignition point | 240 °C lower explosive limit | 0.7% (concentration in air) upper explosive limit | 4% (concentration in air)

DOT hazard class | 6.1 DOT numbers | 1654
Toxicity properties
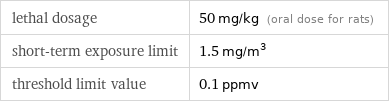
lethal dosage | 50 mg/kg (oral dose for rats) short-term exposure limit | 1.5 mg/m^3 threshold limit value | 0.1 ppmv

probable lethal dose for man | 4 mL (milliliters) long-term exposure limit | 0.5 mg/m^3 (over 8 hours) RTECS classes | agricultural chemical and pesticide | mutagen | reproductive effector | human data | natural product