Input interpretation

tetrafluoroaniline | melting point
Result

-29.48 °C (degrees Celsius) (computed using the Joback method)
Unit conversions
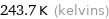
243.7 K (kelvins)

-21.06 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)
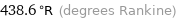
438.6 °R (degrees Rankine)
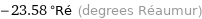
-23.58 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)

-7.977 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparisons as temperature

44.48 °C below temperature at STP (standard temperature and pressure), using the convention of European and South American natural gas companies (15 °C)
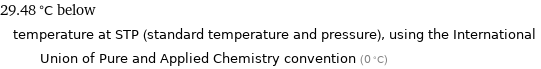
29.48 °C below temperature at STP (standard temperature and pressure), using the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry convention (0 °C)

11.7 °C below temperature of the ice/salt mixture defining the zero point of the Fahrenheit temperature scale (0 °F)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 21 meV (millielectronvolts)
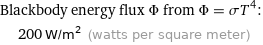
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 200 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 5.9×10^-28 lx (lux)