Input interpretation
phosphorus pentachloride
Chemical names and formulas
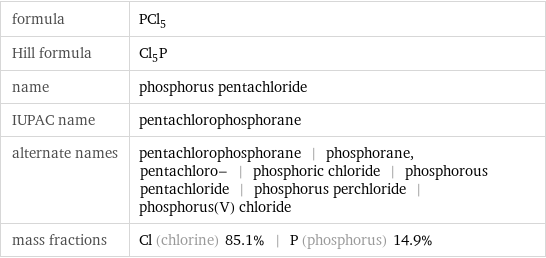
formula | PCl_5 Hill formula | Cl_5P name | phosphorus pentachloride IUPAC name | pentachlorophosphorane alternate names | pentachlorophosphorane | phosphorane, pentachloro- | phosphoric chloride | phosphorous pentachloride | phosphorus perchloride | phosphorus(V) chloride mass fractions | Cl (chlorine) 85.1% | P (phosphorus) 14.9%
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of phosphorus pentachloride. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the chlorine (n_Cl, val = 7) and phosphorus (n_P, val = 5) atoms: 5 n_Cl, val + n_P, val = 40 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for chlorine (n_Cl, full = 8) and phosphorus (n_P, full = 8): 5 n_Cl, full + n_P, full = 48 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 48 - 40 = 8 bonding electrons are needed, which are already accounted for in the structure. Note that the valence shell of phosphorus has been expanded to 5 bonds. After accounting for the expanded valence, there are 5 bonds and hence 10 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 40 - 10 = 30 electrons left to draw: Answer: | |
Basic properties
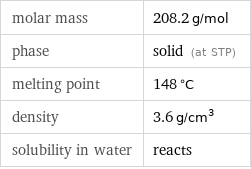
molar mass | 208.2 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 148 °C density | 3.6 g/cm^3 solubility in water | reacts
Units

Solid properties (at STP)

density | 3.6 g/cm^3
Units

Thermodynamic properties
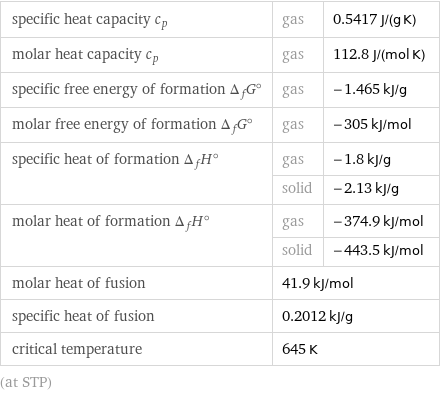
specific heat capacity c_p | gas | 0.5417 J/(g K) molar heat capacity c_p | gas | 112.8 J/(mol K) specific free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gas | -1.465 kJ/g molar free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gas | -305 kJ/mol specific heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | -1.8 kJ/g | solid | -2.13 kJ/g molar heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | -374.9 kJ/mol | solid | -443.5 kJ/mol molar heat of fusion | 41.9 kJ/mol | specific heat of fusion | 0.2012 kJ/g | critical temperature | 645 K | (at STP)
Chemical identifiers
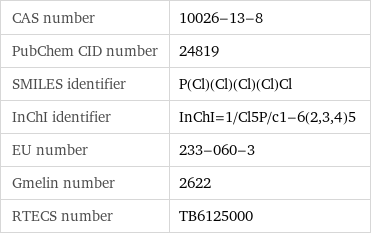
CAS number | 10026-13-8 PubChem CID number | 24819 SMILES identifier | P(Cl)(Cl)(Cl)(Cl)Cl InChI identifier | InChI=1/Cl5P/c1-6(2, 3, 4)5 EU number | 233-060-3 Gmelin number | 2622 RTECS number | TB6125000
NFPA label

NFPA label
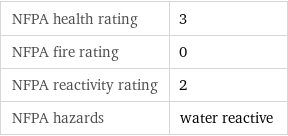
NFPA health rating | 3 NFPA fire rating | 0 NFPA reactivity rating | 2 NFPA hazards | water reactive
Toxicity properties
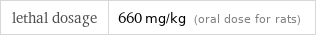
lethal dosage | 660 mg/kg (oral dose for rats)
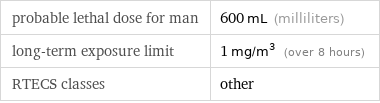
probable lethal dose for man | 600 mL (milliliters) long-term exposure limit | 1 mg/m^3 (over 8 hours) RTECS classes | other