Input interpretation

thermal Doppler broadening
Equation
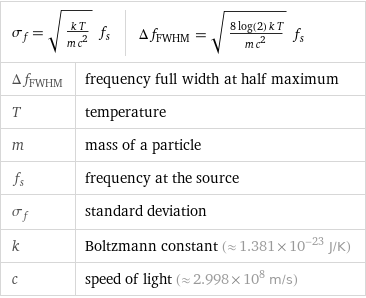
σ_f = sqrt((k T)/(m c^2)) f_s | Δf_FWHM = sqrt((8 log(2) k T)/(m c^2)) f_s | Δf_FWHM | frequency full width at half maximum T | temperature m | mass of a particle f_s | frequency at the source σ_f | standard deviation k | Boltzmann constant (≈ 1.381×10^-23 J/K) c | speed of light (≈ 2.998×10^8 m/s)
Input values
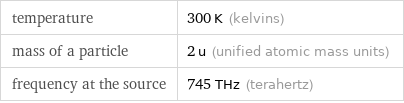
temperature | 300 K (kelvins) mass of a particle | 2 u (unified atomic mass units) frequency at the source | 745 THz (terahertz)
Results

frequency full width at half maximum | 6.535 GHz (gigahertz) = 6.535×10^9 Hz (hertz) = 0.006535 THz (terahertz) standard deviation | 2.775 GHz (gigahertz) = 2.775×10^9 Hz (hertz) = 0.002775 THz (terahertz)
Probability density formula
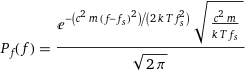
P_f(f) = (e^(-(c^2 m (f - f_s)^2)/(2 k T f_s^2)) sqrt((c^2 m)/(k T f_s)))/sqrt(2 π)