Input interpretation
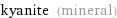
kyanite (mineral)
Image

Image
General properties
![alternate names | cyanite | distene | disthene | rhaeticite formula | Al_2SiO_5=Al[6]Al[6]OSiO_4](../image_source/168d16d700357c22a1a9fa1156779ef2.png)
alternate names | cyanite | distene | disthene | rhaeticite formula | Al_2SiO_5=Al[6]Al[6]OSiO_4
Basic properties
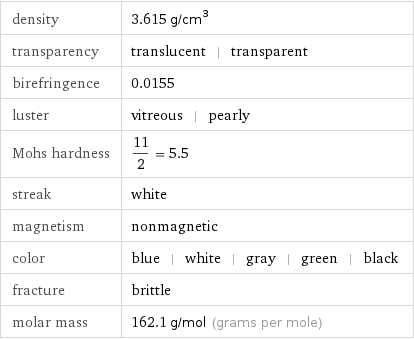
density | 3.615 g/cm^3 transparency | translucent | transparent birefringence | 0.0155 luster | vitreous | pearly Mohs hardness | 11/2 = 5.5 streak | white magnetism | nonmagnetic color | blue | white | gray | green | black fracture | brittle molar mass | 162.1 g/mol (grams per mole)
Units

Mineral identifiers
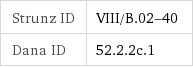
Strunz ID | VIII/B.02-40 Dana ID | 52.2.2c.1
Crystallographic properties
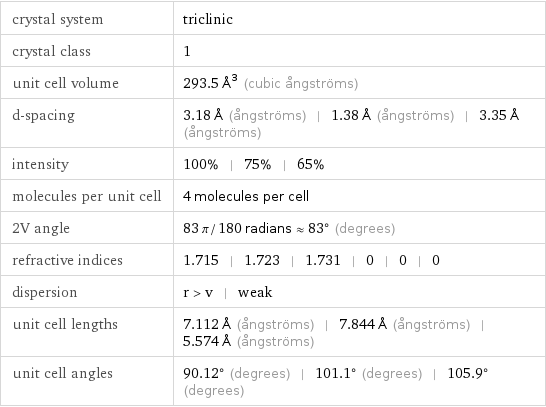
crystal system | triclinic crystal class | 1 unit cell volume | 293.5 Å^3 (cubic ångströms) d-spacing | 3.18 Å (ångströms) | 1.38 Å (ångströms) | 3.35 Å (ångströms) intensity | 100% | 75% | 65% molecules per unit cell | 4 molecules per cell 2V angle | 83 π/180 radians≈83° (degrees) refractive indices | 1.715 | 1.723 | 1.731 | 0 | 0 | 0 dispersion | r > v | weak unit cell lengths | 7.112 Å (ångströms) | 7.844 Å (ångströms) | 5.574 Å (ångströms) unit cell angles | 90.12° (degrees) | 101.1° (degrees) | 105.9° (degrees)
Wikipedia summary

Kyanite is typically a blue aluminosilicate mineral, usually found in aluminium-rich metamorphic pegmatites and/or sedimentary rock. Kyanite in metamorphic rocks generally indicates pressures higher than four kilobars. It is commonly found in quartz. Although potentially stable at lower pressure and low temperature, the activity of water is usually high enough under such conditions that it is replaced by hydrous aluminosilicates such as muscovite, pyrophyllite, or kaolinite. Kyanite is also known as disthene, rhaeticite and cyanite.