Input interpretation

strong bases | molar mass
Summary
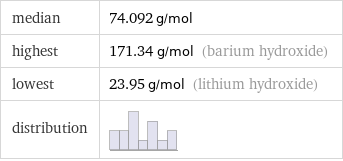
median | 74.092 g/mol highest | 171.34 g/mol (barium hydroxide) lowest | 23.95 g/mol (lithium hydroxide) distribution |
Units

Distribution plots
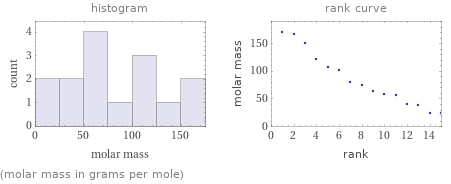
(molar mass in grams per mole)
Molar mass rankings
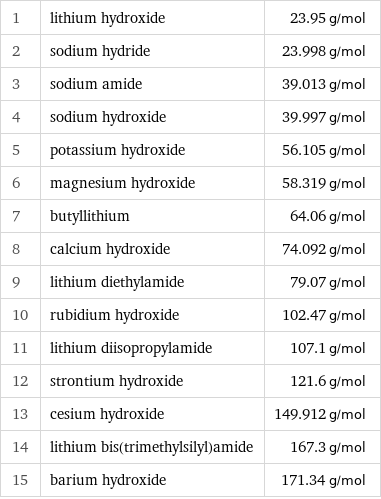
1 | lithium hydroxide | 23.95 g/mol 2 | sodium hydride | 23.998 g/mol 3 | sodium amide | 39.013 g/mol 4 | sodium hydroxide | 39.997 g/mol 5 | potassium hydroxide | 56.105 g/mol 6 | magnesium hydroxide | 58.319 g/mol 7 | butyllithium | 64.06 g/mol 8 | calcium hydroxide | 74.092 g/mol 9 | lithium diethylamide | 79.07 g/mol 10 | rubidium hydroxide | 102.47 g/mol 11 | lithium diisopropylamide | 107.1 g/mol 12 | strontium hydroxide | 121.6 g/mol 13 | cesium hydroxide | 149.912 g/mol 14 | lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide | 167.3 g/mol 15 | barium hydroxide | 171.34 g/mol
Unit conversion for median molar mass 74.092 g/mol
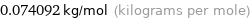
0.074092 kg/mol (kilograms per mole)
Comparisons for median molar mass 74.092 g/mol
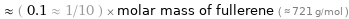
≈ ( 0.1 ≈ 1/10 ) × molar mass of fullerene ( ≈ 721 g/mol )
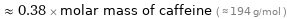
≈ 0.38 × molar mass of caffeine ( ≈ 194 g/mol )
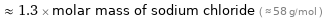
≈ 1.3 × molar mass of sodium chloride ( ≈ 58 g/mol )
Corresponding quantities
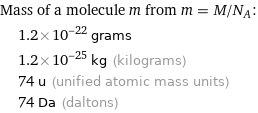
Mass of a molecule m from m = M/N_A: | 1.2×10^-22 grams | 1.2×10^-25 kg (kilograms) | 74 u (unified atomic mass units) | 74 Da (daltons)
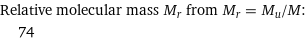
Relative molecular mass M_r from M_r = M_u/M: | 74