Input interpretation

nonafluorobutane sulfonate
Basic properties
![molar mass | 299.1 g/mol formula | (C_4F_9O_3S)^- empirical formula | F_9C_4S_O_3 SMILES identifier | C(C(C(F)(F)S(=O)(=O)[O-])(F)F)(C(F)(F)F)(F)F InChI identifier | InChI=1/C4HF9O3S/c5-1(6, 3(9, 10)11)2(7, 8)4(12, 13)17(14, 15)16/h(H, 14, 15, 16)/p-1/fC4F9O3S/q-1 InChI key | JGTNAGYHADQMCM-UHFFFAOYSA-M](../image_source/09ef16d50c8d84ed8feaa9714cb62bc6.png)
molar mass | 299.1 g/mol formula | (C_4F_9O_3S)^- empirical formula | F_9C_4S_O_3 SMILES identifier | C(C(C(F)(F)S(=O)(=O)[O-])(F)F)(C(F)(F)F)(F)F InChI identifier | InChI=1/C4HF9O3S/c5-1(6, 3(9, 10)11)2(7, 8)4(12, 13)17(14, 15)16/h(H, 14, 15, 16)/p-1/fC4F9O3S/q-1 InChI key | JGTNAGYHADQMCM-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Lewis structure
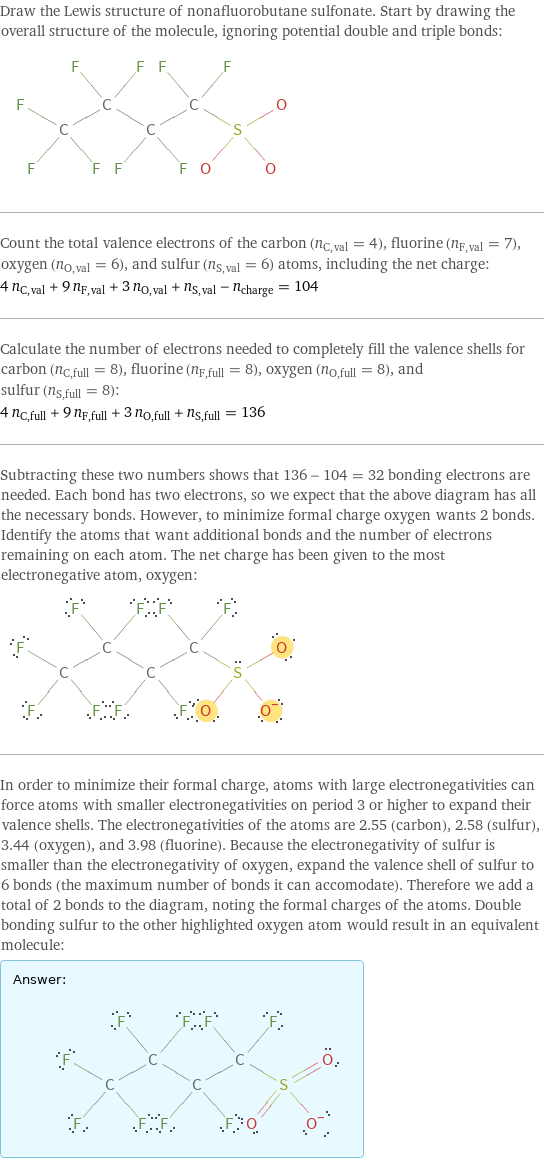
Draw the Lewis structure of nonafluorobutane sulfonate. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), fluorine (n_F, val = 7), oxygen (n_O, val = 6), and sulfur (n_S, val = 6) atoms, including the net charge: 4 n_C, val + 9 n_F, val + 3 n_O, val + n_S, val - n_charge = 104 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), fluorine (n_F, full = 8), oxygen (n_O, full = 8), and sulfur (n_S, full = 8): 4 n_C, full + 9 n_F, full + 3 n_O, full + n_S, full = 136 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 136 - 104 = 32 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so we expect that the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. However, to minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom. The net charge has been given to the most electronegative atom, oxygen: In order to minimize their formal charge, atoms with large electronegativities can force atoms with smaller electronegativities on period 3 or higher to expand their valence shells. The electronegativities of the atoms are 2.55 (carbon), 2.58 (sulfur), 3.44 (oxygen), and 3.98 (fluorine). Because the electronegativity of sulfur is smaller than the electronegativity of oxygen, expand the valence shell of sulfur to 6 bonds (the maximum number of bonds it can accomodate). Therefore we add a total of 2 bonds to the diagram, noting the formal charges of the atoms. Double bonding sulfur to the other highlighted oxygen atom would result in an equivalent molecule: Answer: | |
Quantitative molecular descriptors
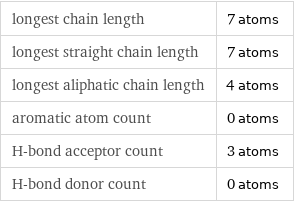
longest chain length | 7 atoms longest straight chain length | 7 atoms longest aliphatic chain length | 4 atoms aromatic atom count | 0 atoms H-bond acceptor count | 3 atoms H-bond donor count | 0 atoms
Elemental composition
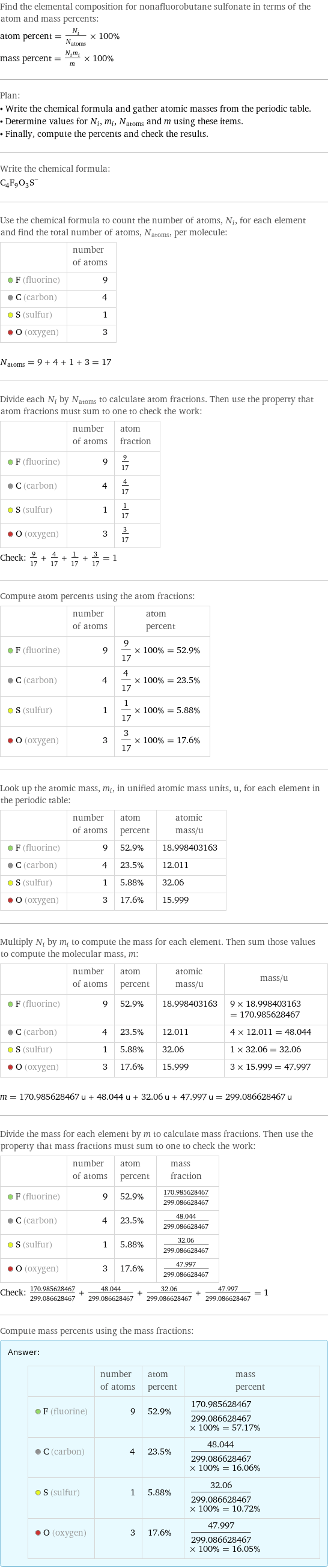
Find the elemental composition for nonafluorobutane sulfonate in terms of the atom and mass percents: atom percent = N_i/N_atoms × 100% mass percent = (N_im_i)/m × 100% Plan: • Write the chemical formula and gather atomic masses from the periodic table. • Determine values for N_i, m_i, N_atoms and m using these items. • Finally, compute the percents and check the results. Write the chemical formula: (C_4F_9O_3S)^- Use the chemical formula to count the number of atoms, N_i, for each element and find the total number of atoms, N_atoms, per molecule: | number of atoms F (fluorine) | 9 C (carbon) | 4 S (sulfur) | 1 O (oxygen) | 3 N_atoms = 9 + 4 + 1 + 3 = 17 Divide each N_i by N_atoms to calculate atom fractions. Then use the property that atom fractions must sum to one to check the work: | number of atoms | atom fraction F (fluorine) | 9 | 9/17 C (carbon) | 4 | 4/17 S (sulfur) | 1 | 1/17 O (oxygen) | 3 | 3/17 Check: 9/17 + 4/17 + 1/17 + 3/17 = 1 Compute atom percents using the atom fractions: | number of atoms | atom percent F (fluorine) | 9 | 9/17 × 100% = 52.9% C (carbon) | 4 | 4/17 × 100% = 23.5% S (sulfur) | 1 | 1/17 × 100% = 5.88% O (oxygen) | 3 | 3/17 × 100% = 17.6% Look up the atomic mass, m_i, in unified atomic mass units, u, for each element in the periodic table: | number of atoms | atom percent | atomic mass/u F (fluorine) | 9 | 52.9% | 18.998403163 C (carbon) | 4 | 23.5% | 12.011 S (sulfur) | 1 | 5.88% | 32.06 O (oxygen) | 3 | 17.6% | 15.999 Multiply N_i by m_i to compute the mass for each element. Then sum those values to compute the molecular mass, m: | number of atoms | atom percent | atomic mass/u | mass/u F (fluorine) | 9 | 52.9% | 18.998403163 | 9 × 18.998403163 = 170.985628467 C (carbon) | 4 | 23.5% | 12.011 | 4 × 12.011 = 48.044 S (sulfur) | 1 | 5.88% | 32.06 | 1 × 32.06 = 32.06 O (oxygen) | 3 | 17.6% | 15.999 | 3 × 15.999 = 47.997 m = 170.985628467 u + 48.044 u + 32.06 u + 47.997 u = 299.086628467 u Divide the mass for each element by m to calculate mass fractions. Then use the property that mass fractions must sum to one to check the work: | number of atoms | atom percent | mass fraction F (fluorine) | 9 | 52.9% | 170.985628467/299.086628467 C (carbon) | 4 | 23.5% | 48.044/299.086628467 S (sulfur) | 1 | 5.88% | 32.06/299.086628467 O (oxygen) | 3 | 17.6% | 47.997/299.086628467 Check: 170.985628467/299.086628467 + 48.044/299.086628467 + 32.06/299.086628467 + 47.997/299.086628467 = 1 Compute mass percents using the mass fractions: Answer: | | | number of atoms | atom percent | mass percent F (fluorine) | 9 | 52.9% | 170.985628467/299.086628467 × 100% = 57.17% C (carbon) | 4 | 23.5% | 48.044/299.086628467 × 100% = 16.06% S (sulfur) | 1 | 5.88% | 32.06/299.086628467 × 100% = 10.72% O (oxygen) | 3 | 17.6% | 47.997/299.086628467 × 100% = 16.05%
Elemental oxidation states
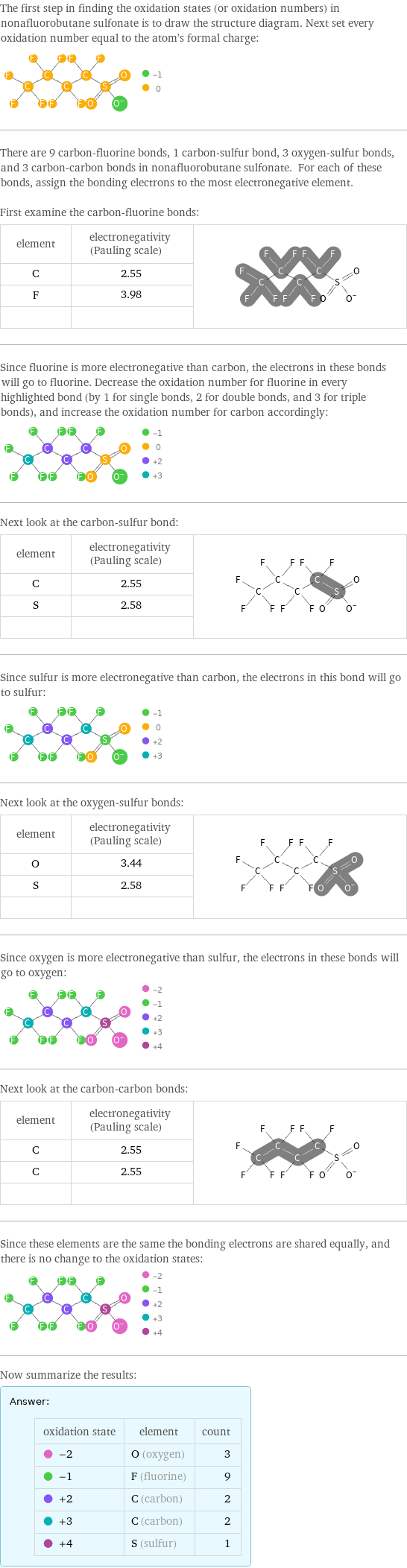
The first step in finding the oxidation states (or oxidation numbers) in nonafluorobutane sulfonate is to draw the structure diagram. Next set every oxidation number equal to the atom's formal charge: There are 9 carbon-fluorine bonds, 1 carbon-sulfur bond, 3 oxygen-sulfur bonds, and 3 carbon-carbon bonds in nonafluorobutane sulfonate. For each of these bonds, assign the bonding electrons to the most electronegative element. First examine the carbon-fluorine bonds: element | electronegativity (Pauling scale) | C | 2.55 | F | 3.98 | | | Since fluorine is more electronegative than carbon, the electrons in these bonds will go to fluorine. Decrease the oxidation number for fluorine in every highlighted bond (by 1 for single bonds, 2 for double bonds, and 3 for triple bonds), and increase the oxidation number for carbon accordingly: Next look at the carbon-sulfur bond: element | electronegativity (Pauling scale) | C | 2.55 | S | 2.58 | | | Since sulfur is more electronegative than carbon, the electrons in this bond will go to sulfur: Next look at the oxygen-sulfur bonds: element | electronegativity (Pauling scale) | O | 3.44 | S | 2.58 | | | Since oxygen is more electronegative than sulfur, the electrons in these bonds will go to oxygen: Next look at the carbon-carbon bonds: element | electronegativity (Pauling scale) | C | 2.55 | C | 2.55 | | | Since these elements are the same the bonding electrons are shared equally, and there is no change to the oxidation states: Now summarize the results: Answer: | | oxidation state | element | count -2 | O (oxygen) | 3 -1 | F (fluorine) | 9 +2 | C (carbon) | 2 +3 | C (carbon) | 2 +4 | S (sulfur) | 1
Orbital hybridization
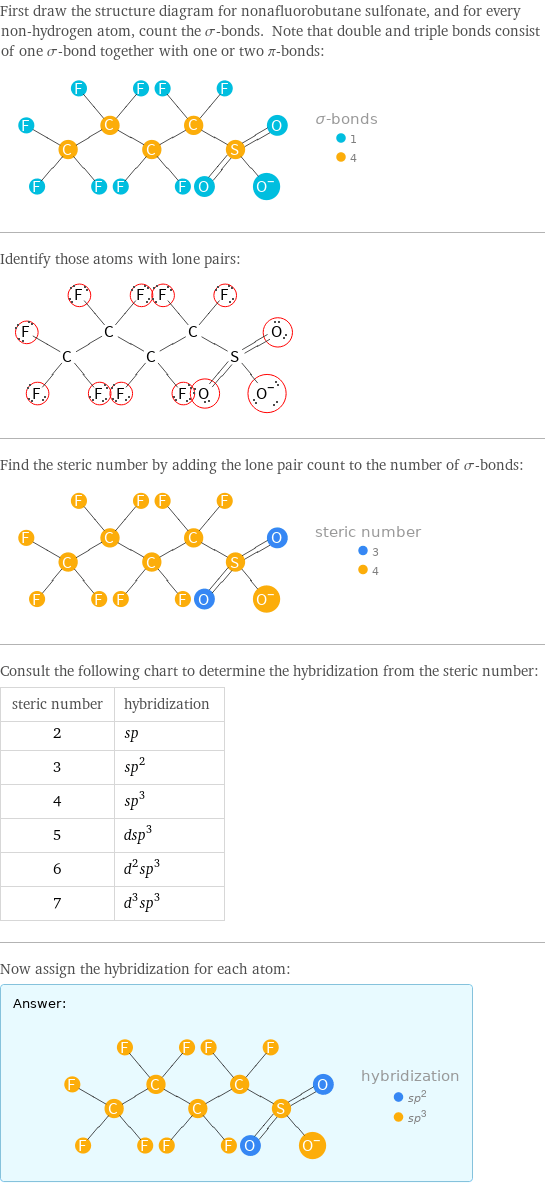
First draw the structure diagram for nonafluorobutane sulfonate, and for every non-hydrogen atom, count the σ-bonds. Note that double and triple bonds consist of one σ-bond together with one or two π-bonds: Identify those atoms with lone pairs: Find the steric number by adding the lone pair count to the number of σ-bonds: Consult the following chart to determine the hybridization from the steric number: steric number | hybridization 2 | sp 3 | sp^2 4 | sp^3 5 | dsp^3 6 | d^2sp^3 7 | d^3sp^3 Now assign the hybridization for each atom: Answer: | |
Topological indices
vertex count | 17 edge count | 16 Schultz index | 1564 Wiener index | 436 Hosoya index | 611 Balaban index | 5.733