Input interpretation
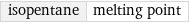
isopentane | melting point
Result
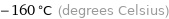
-160 °C (degrees Celsius)
Phase diagram
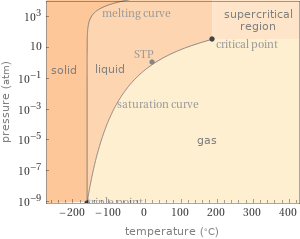
Phase diagram
Units

Unit conversions
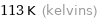
113 K (kelvins)

-256 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)

204 °R (degrees Rankine)
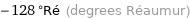
-128 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)

-76.5 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparisons as temperature
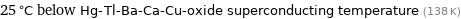
25 °C below Hg-Tl-Ba-Ca-Cu-oxide superconducting temperature (138 K)
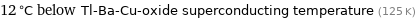
12 °C below Tl-Ba-Cu-oxide superconducting temperature (125 K)
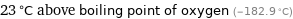
23 °C above boiling point of oxygen (-182.9 °C)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 9.8 meV (millielectronvolts)
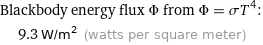
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 9.3 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 1.2×10^-66 lx (lux)