Input interpretation
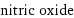
nitric oxide
Chemical names and formulas

formula | NO name | nitric oxide alternate names | EDRF | endothelium derived relaxing factor | nitrogen monoxide | nitrogen oxide | nitrosyl radical | No mass fractions | N (nitrogen) 46.7% | O (oxygen) 53.3%
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of nitric oxide. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the nitrogen (n_N, val = 5) and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: n_N, val + n_O, val = 11 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for nitrogen (n_N, full = 8) and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): n_N, full + n_O, full = 16 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 16 - 11 = 5 bonding electrons are expected (in such cases with an odd number, round down to 4 bonding electrons). Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 1 bond already present in the diagram add 1 bond. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 1 bond by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms: Answer: | |
Basic properties
molar mass | 30.006 g/mol phase | gas (at STP) melting point | -163.6 °C boiling point | -151.7 °C density | 0.001226 g/cm^3 (at 25 °C) dielectric constant | 1.001
Hydrophobicity and permeability properties
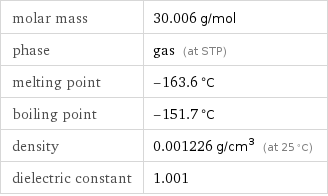
experimental LogP hydrophobicity | 0
Basic drug properties

approval status | approved | small molecule drug categories | bronchodilator agent | endothelium-dependent relaxing factor | free radical scavenger dosage forms | respiratory (inhalation): gas

brand names | amidogen, oxo- | INomax | mononitrogen monoxide | NMO | NO | nitric oxide 10% by volume or more | nitric oxide trimer | nitrogen monooxide | nitrogen monoxide | nitrogen oxide | nitrosyl radical | RCRA waste number P076 | nitrogen protoxide
Gas properties (at STP)
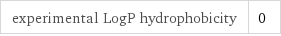
density | 0.001226 g/cm^3 (at 25 °C) vapor density | 1.05 (relative to air) molar volume | 24470 cm^3/mol refractive index | 1.0002697 dynamic viscosity | 1.911×10^-5 Pa s (at 25 °C)
Units

Liquid properties (-151.7 °C)

sound speed | 1170 km/h (at 10 °C (degrees Celsius))
Units

Thermodynamic properties
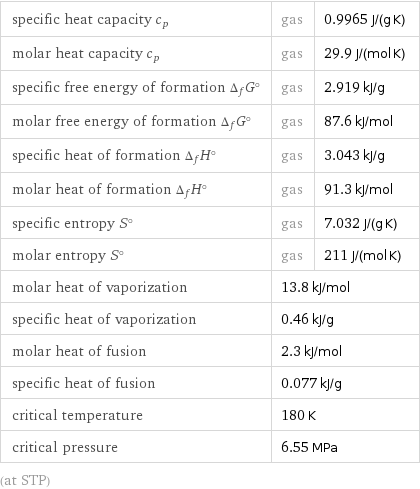
specific heat capacity c_p | gas | 0.9965 J/(g K) molar heat capacity c_p | gas | 29.9 J/(mol K) specific free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gas | 2.919 kJ/g molar free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gas | 87.6 kJ/mol specific heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | 3.043 kJ/g molar heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | 91.3 kJ/mol specific entropy S° | gas | 7.032 J/(g K) molar entropy S° | gas | 211 J/(mol K) molar heat of vaporization | 13.8 kJ/mol | specific heat of vaporization | 0.46 kJ/g | molar heat of fusion | 2.3 kJ/mol | specific heat of fusion | 0.077 kJ/g | critical temperature | 180 K | critical pressure | 6.55 MPa | (at STP)