Input interpretation
tetrahydrocannabinol
Chemical names and formulas
![formula | C_21H_30O_2 name | tetrahydrocannabinol IUPAC name | (6aR, 10aR)-6, 6, 9-trimethyl-3-pentyl-6a, 7, 8, 10a-tetrahydrobenzo[c]chromen-1-ol alternate names | delta 9-THC | Dronabinol | marinol | THC mass fractions | C (carbon) 80.2% | H (hydrogen) 9.62% | O (oxygen) 10.2%](../image_source/01b92dbae6412d8f25a4755167786de8.png)
formula | C_21H_30O_2 name | tetrahydrocannabinol IUPAC name | (6aR, 10aR)-6, 6, 9-trimethyl-3-pentyl-6a, 7, 8, 10a-tetrahydrobenzo[c]chromen-1-ol alternate names | delta 9-THC | Dronabinol | marinol | THC mass fractions | C (carbon) 80.2% | H (hydrogen) 9.62% | O (oxygen) 10.2%
Lewis structure
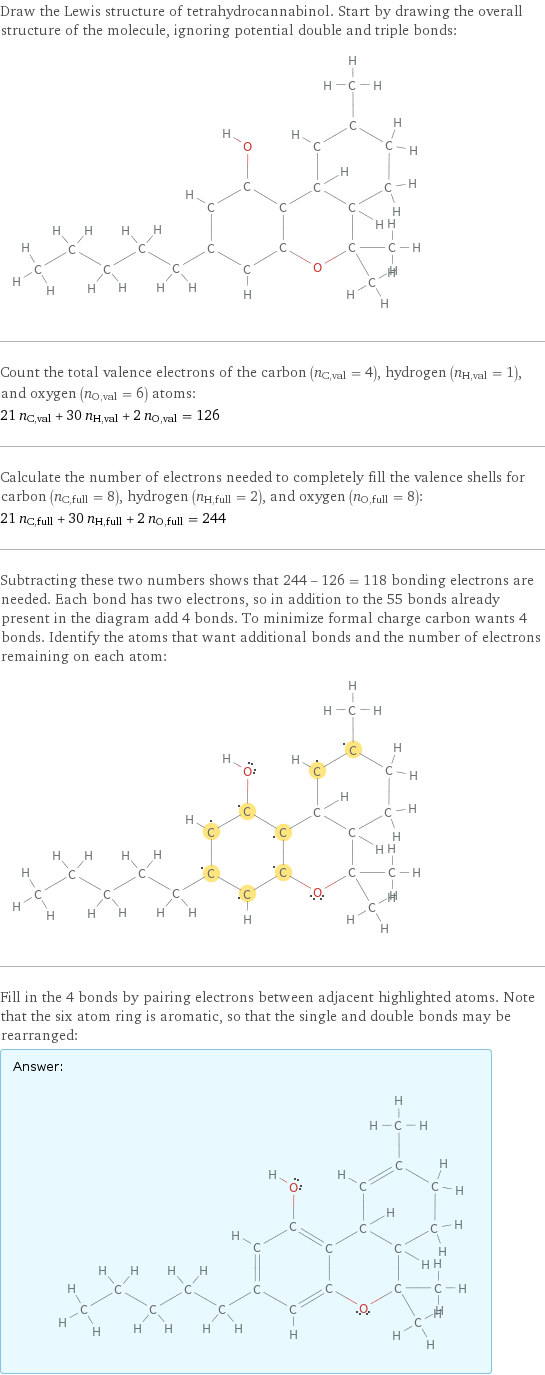
Draw the Lewis structure of tetrahydrocannabinol. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 21 n_C, val + 30 n_H, val + 2 n_O, val = 126 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 21 n_C, full + 30 n_H, full + 2 n_O, full = 244 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 244 - 126 = 118 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 55 bonds already present in the diagram add 4 bonds. To minimize formal charge carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 4 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms. Note that the six atom ring is aromatic, so that the single and double bonds may be rearranged: Answer: | |
3D structure
3D structure
Basic properties
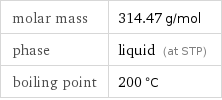
molar mass | 314.47 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) boiling point | 200 °C
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties

experimental LogP hydrophobicity | 5.65 predicted LogP hydrophobicity | 7.29 predicted LogS | -5.08
Basic drug properties

approval status | approved | illicit | small molecule drug categories | analgesic | non-narcotic analgesic | antiemetic | hallucinogen | psychotropic drug dosage forms | oral: capsule
![brand names | delta 9-THC | delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol | abbott 40566 | dea No. 7369 | dea No. 7370 | deltanyne | marinol | dronabinol | dronabinol [usan:inn] | delta-9-THC | delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol addiction potential of drug | 21.1%](../image_source/fea7b21773fb7c531079fd10e3a14bc8.png)
brand names | delta 9-THC | delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol | abbott 40566 | dea No. 7369 | dea No. 7370 | deltanyne | marinol | dronabinol | dronabinol [usan:inn] | delta-9-THC | delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol addiction potential of drug | 21.1%
Chemical identifiers
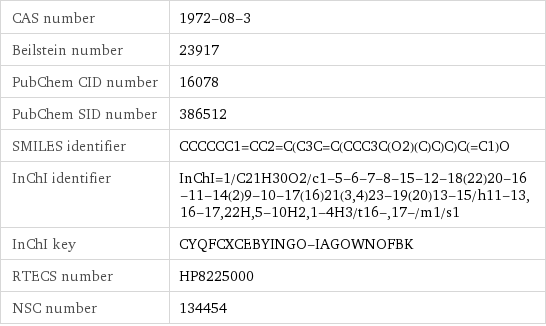
CAS number | 1972-08-3 Beilstein number | 23917 PubChem CID number | 16078 PubChem SID number | 386512 SMILES identifier | CCCCCC1=CC2=C(C3C=C(CCC3C(O2)(C)C)C)C(=C1)O InChI identifier | InChI=1/C21H30O2/c1-5-6-7-8-15-12-18(22)20-16-11-14(2)9-10-17(16)21(3, 4)23-19(20)13-15/h11-13, 16-17, 22H, 5-10H2, 1-4H3/t16-, 17-/m1/s1 InChI key | CYQFCXCEBYINGO-IAGOWNOFBK RTECS number | HP8225000 NSC number | 134454
Toxicity properties
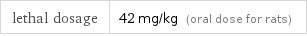
lethal dosage | 42 mg/kg (oral dose for rats)

probable lethal dose for man | 4 mL (milliliters) RTECS classes | tumorigen | drug | mutagen | reproductive effector | natural product