Input interpretation

insulators | melting point
Summary

median | 113.7 °C highest | 2075 °C (boron) lowest | -101.5 °C (chlorine) distribution |
Plot
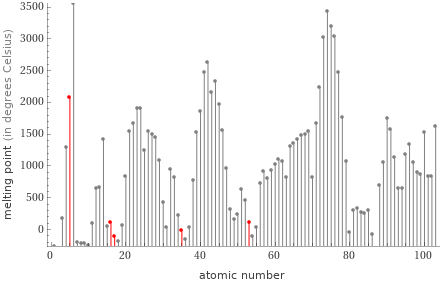
Plot
Melting point rankings
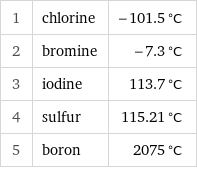
1 | chlorine | -101.5 °C 2 | bromine | -7.3 °C 3 | iodine | 113.7 °C 4 | sulfur | 115.21 °C 5 | boron | 2075 °C
Unit conversions for median melting point 113.7 °C
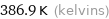
386.9 K (kelvins)

236.7 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)
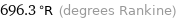
696.3 °R (degrees Rankine)
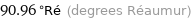
90.96 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)

67.19 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median melting point 113.7 °C
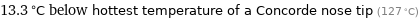
13.3 °C below hottest temperature of a Concorde nose tip (127 °C)
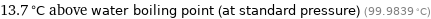
13.7 °C above water boiling point (at standard pressure) (99.9839 °C)
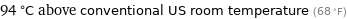
94 °C above conventional US room temperature (68 °F)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 33 meV (millielectronvolts)
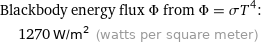
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 1270 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 6.4×10^-15 lx (lux)
Thermodynamic properties
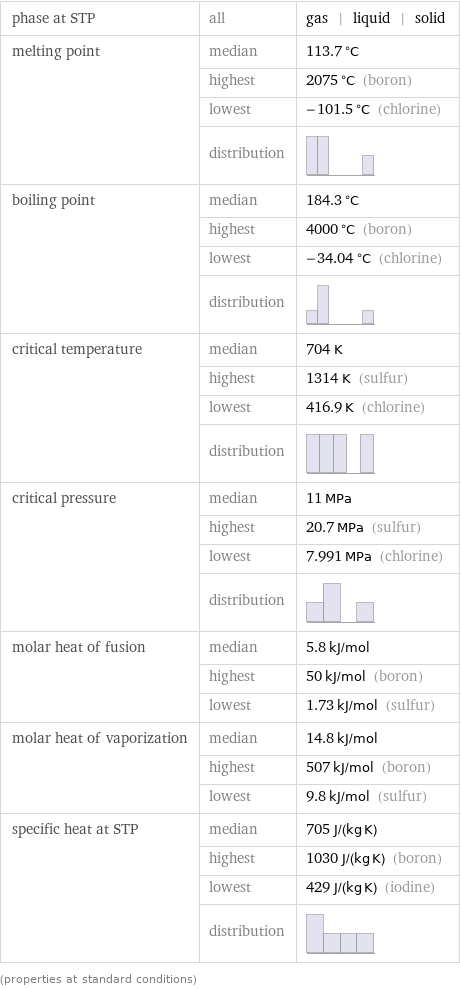
phase at STP | all | gas | liquid | solid melting point | median | 113.7 °C | highest | 2075 °C (boron) | lowest | -101.5 °C (chlorine) | distribution | boiling point | median | 184.3 °C | highest | 4000 °C (boron) | lowest | -34.04 °C (chlorine) | distribution | critical temperature | median | 704 K | highest | 1314 K (sulfur) | lowest | 416.9 K (chlorine) | distribution | critical pressure | median | 11 MPa | highest | 20.7 MPa (sulfur) | lowest | 7.991 MPa (chlorine) | distribution | molar heat of fusion | median | 5.8 kJ/mol | highest | 50 kJ/mol (boron) | lowest | 1.73 kJ/mol (sulfur) molar heat of vaporization | median | 14.8 kJ/mol | highest | 507 kJ/mol (boron) | lowest | 9.8 kJ/mol (sulfur) specific heat at STP | median | 705 J/(kg K) | highest | 1030 J/(kg K) (boron) | lowest | 429 J/(kg K) (iodine) | distribution | (properties at standard conditions)
Nearest corresponding gas marks for median melting point 113.7 °C (degrees Celsius)
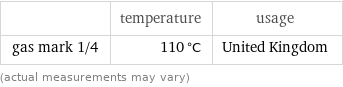
| temperature | usage gas mark 1/4 | 110 °C | United Kingdom (actual measurements may vary)