Input interpretation
metatrexan
Chemical names and formulas
![formula | C_20H_22N_8O_5 name | metatrexan IUPAC name | (2R)-2-[[4-[(2, 4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl-methyl-amino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid alternate names | 4-amino-10-methylfolic acid | amethopterin | amethopterine | antifolan | ledertrexate | methotrexate | mexate | rheumatrex mass fractions | C (carbon) 52.9% | H (hydrogen) 4.88% | N (nitrogen) 24.7% | O (oxygen) 17.6%](../image_source/379f0c6881e6a061b112301b61a7e74d.png)
formula | C_20H_22N_8O_5 name | metatrexan IUPAC name | (2R)-2-[[4-[(2, 4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl-methyl-amino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid alternate names | 4-amino-10-methylfolic acid | amethopterin | amethopterine | antifolan | ledertrexate | methotrexate | mexate | rheumatrex mass fractions | C (carbon) 52.9% | H (hydrogen) 4.88% | N (nitrogen) 24.7% | O (oxygen) 17.6%
Lewis structure
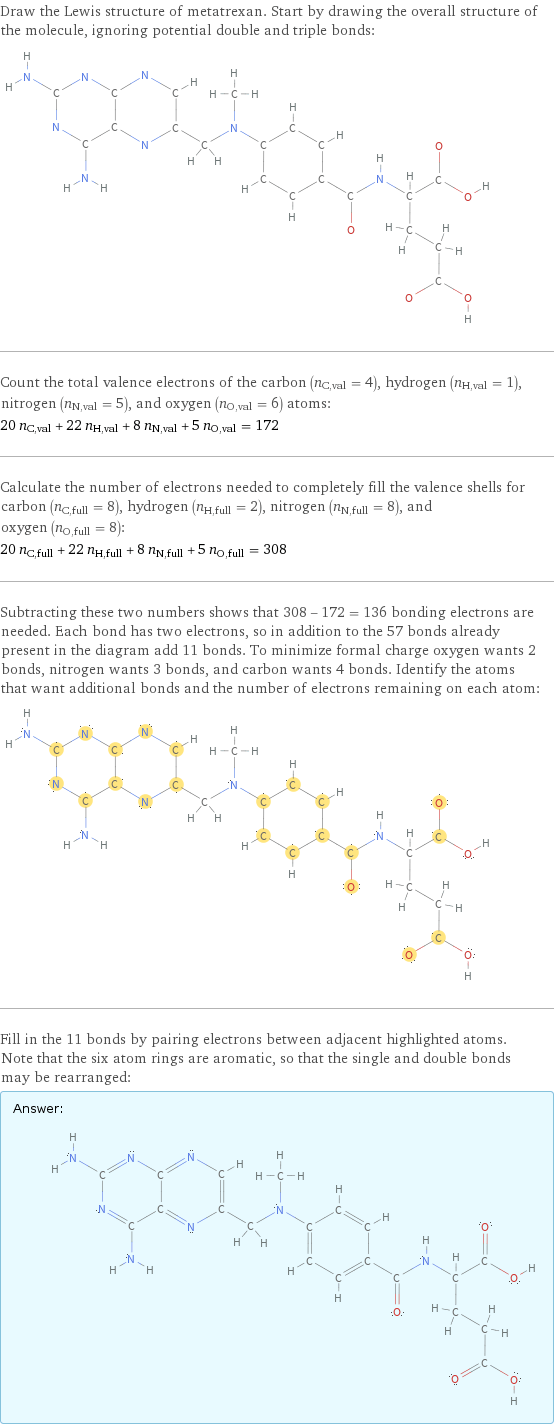
Draw the Lewis structure of metatrexan. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 20 n_C, val + 22 n_H, val + 8 n_N, val + 5 n_O, val = 172 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 20 n_C, full + 22 n_H, full + 8 n_N, full + 5 n_O, full = 308 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 308 - 172 = 136 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 57 bonds already present in the diagram add 11 bonds. To minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds, nitrogen wants 3 bonds, and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 11 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms. Note that the six atom rings are aromatic, so that the single and double bonds may be rearranged: Answer: | |
3D structure
3D structure
Basic properties
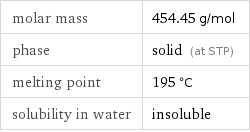
molar mass | 454.45 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 195 °C solubility in water | insoluble
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties

experimental LogP hydrophobicity | -2.2 predicted LogP hydrophobicity | -0.91 predicted LogS | -3.42 experimental Caco-2 permeability | -5.92
Drug interactions

acitretin | amoxicillin | ampicillin | aspirin | bacampicillin | bismuth subsalicylate | carbenicillin | cholestyramine | 3-quinolinecarboxylic acid | cis-diamminedichloridoplatinum(II) | cloxacillin | cyclosporin A | diclofenac | dicloxacillin | digoxin | doxycycline | ethotoin | etodolac | etretinate | fenoprofen | ... (total: 69)
Basic drug properties
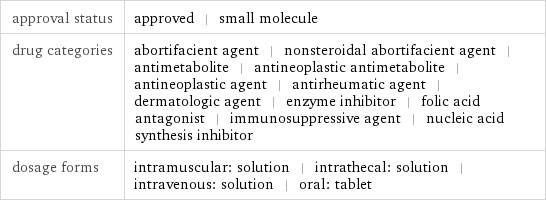
approval status | approved | small molecule drug categories | abortifacient agent | nonsteroidal abortifacient agent | antimetabolite | antineoplastic antimetabolite | antineoplastic agent | antirheumatic agent | dermatologic agent | enzyme inhibitor | folic acid antagonist | immunosuppressive agent | nucleic acid synthesis inhibitor dosage forms | intramuscular: solution | intrathecal: solution | intravenous: solution | oral: tablet

brand names | abitrexate | antifolan | arbitrexate | emtexate | folex | ledertrexate | metatrexan | methotrate | mexate | rheumatrex | trexall
Chemical identifiers
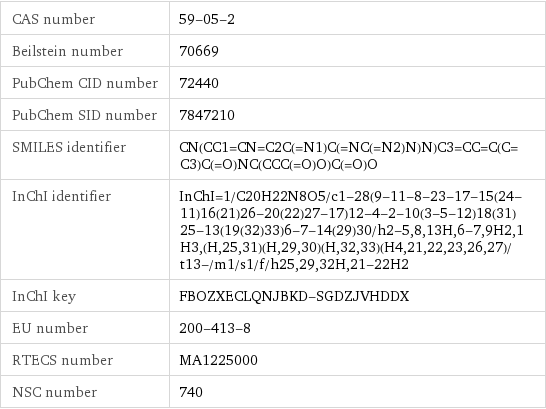
CAS number | 59-05-2 Beilstein number | 70669 PubChem CID number | 72440 PubChem SID number | 7847210 SMILES identifier | CN(CC1=CN=C2C(=N1)C(=NC(=N2)N)N)C3=CC=C(C=C3)C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)O)C(=O)O InChI identifier | InChI=1/C20H22N8O5/c1-28(9-11-8-23-17-15(24-11)16(21)26-20(22)27-17)12-4-2-10(3-5-12)18(31)25-13(19(32)33)6-7-14(29)30/h2-5, 8, 13H, 6-7, 9H2, 1H3, (H, 25, 31)(H, 29, 30)(H, 32, 33)(H4, 21, 22, 23, 26, 27)/t13-/m1/s1/f/h25, 29, 32H, 21-22H2 InChI key | FBOZXECLQNJBKD-SGDZJVHDDX EU number | 200-413-8 RTECS number | MA1225000 NSC number | 740
NFPA label

NFPA label
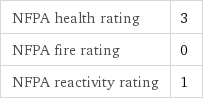
NFPA health rating | 3 NFPA fire rating | 0 NFPA reactivity rating | 1