Input interpretation
2 kg of water
Basic properties for 2 kg
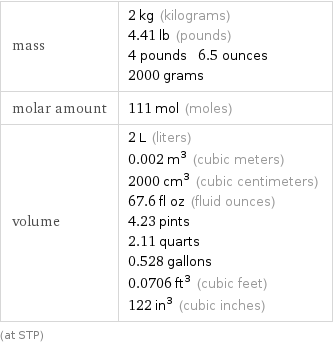
mass | 2 kg (kilograms) 4.41 lb (pounds) 4 pounds 6.5 ounces 2000 grams molar amount | 111 mol (moles) volume | 2 L (liters) 0.002 m^3 (cubic meters) 2000 cm^3 (cubic centimeters) 67.6 fl oz (fluid ounces) 4.23 pints 2.11 quarts 0.528 gallons 0.0706 ft^3 (cubic feet) 122 in^3 (cubic inches) (at STP)
Corresponding quantities
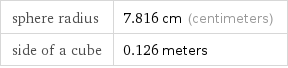
sphere radius | 7.816 cm (centimeters) side of a cube | 0.126 meters
Thermodynamic properties for 2 kg
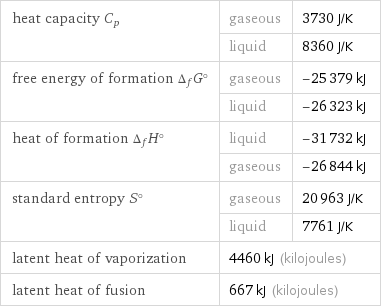
heat capacity C_p | gaseous | 3730 J/K | liquid | 8360 J/K free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gaseous | -25379 kJ | liquid | -26323 kJ heat of formation Δ_fH° | liquid | -31732 kJ | gaseous | -26844 kJ standard entropy S° | gaseous | 20963 J/K | liquid | 7761 J/K latent heat of vaporization | 4460 kJ (kilojoules) | latent heat of fusion | 667 kJ (kilojoules) |
Units

Energy vs. temperature for 2 kg
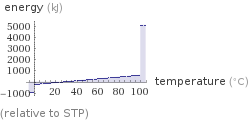
(relative to STP)
Units

Phase change energies for 2 kg from 25 °C

energy required to heat to boiling point | 627 kJ (kilojoules) energy required to convert to vapor | 4460 kJ (kilojoules) energy required to heat to boiling point and convert to vapor | 5090 kJ (kilojoules) energy released from cooling to freezing point | 209 kJ (kilojoules) energy released from converting to solid | 667 kJ (kilojoules) energy released from cooling to freezing point and converting to solid | 876 kJ (kilojoules)
Mass composition for 2 kg
H (hydrogen) | 0.224 kg (11.2%) O (oxygen) | 1.776 kg (88.8%)
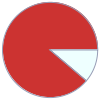
Mass composition for 2 kg
Structure diagram

Structure diagram
Chemical names and formulas
formula | H_2O Hill formula | H_2O name | water IUPAC name | water