Input interpretation

refrigerants | critical temperature
Summary

median | 401.8 K highest | 663 K (pentachloroethane) lowest | 5.19 K (helium) distribution | | (based on 78 values; 15 unavailable)
Entities with missing values

vinyl chloride | chloroethane | 1, 1, 1-trifluoropropane | 1, 1-dichloroethane | 1, 1, 2, 2-tetrafluoroethyl methyl ether | 1, 1, 2, 2, 3-pentafluoropropane | trichlorofluoromethane | 1H-heptafluoropropane | 1, 2-dichlorotetrafluoroethane | 1, 1, 1-trichloro-2, 2, 2-trifluoroethane | ... (total: 15)
Distribution plots
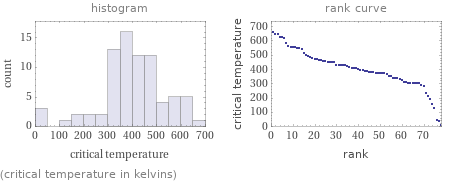
(critical temperature in kelvins)
Critical temperature rankings
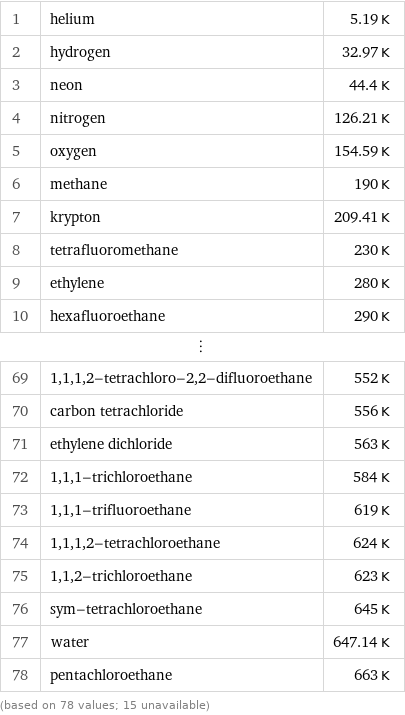
1 | helium | 5.19 K 2 | hydrogen | 32.97 K 3 | neon | 44.4 K 4 | nitrogen | 126.21 K 5 | oxygen | 154.59 K 6 | methane | 190 K 7 | krypton | 209.41 K 8 | tetrafluoromethane | 230 K 9 | ethylene | 280 K 10 | hexafluoroethane | 290 K ⋮ | | 69 | 1, 1, 1, 2-tetrachloro-2, 2-difluoroethane | 552 K 70 | carbon tetrachloride | 556 K 71 | ethylene dichloride | 563 K 72 | 1, 1, 1-trichloroethane | 584 K 73 | 1, 1, 1-trifluoroethane | 619 K 74 | 1, 1, 1, 2-tetrachloroethane | 624 K 75 | 1, 1, 2-trichloroethane | 623 K 76 | sym-tetrachloroethane | 645 K 77 | water | 647.14 K 78 | pentachloroethane | 663 K (based on 78 values; 15 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median critical temperature 401.8 K
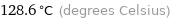
128.6 °C (degrees Celsius)

263.5 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)
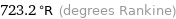
723.2 °R (degrees Rankine)
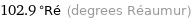
102.9 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)

75.03 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median critical temperature 401.8 K

(90 to 120) K below autoignition temperature of paper (218 to 246 °C)
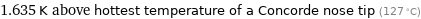
1.635 K above hottest temperature of a Concorde nose tip (127 °C)
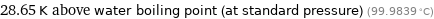
28.65 K above water boiling point (at standard pressure) (99.9839 °C)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 35 meV (millielectronvolts)
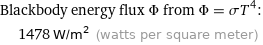
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 1478 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)