Input interpretation
oxidants | melting point
Summary

median | 205 °C highest | 2170 °C (calcium chromate) lowest | -223.9 °C (oxygen difluoride) distribution | | (based on 82 values; 7 unavailable)
Entities with missing values
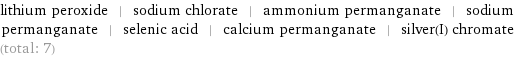
lithium peroxide | sodium chlorate | ammonium permanganate | sodium permanganate | selenic acid | calcium permanganate | silver(I) chromate (total: 7)
Distribution plots
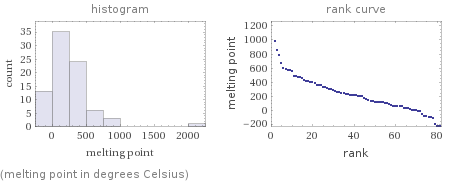
(melting point in degrees Celsius)
Melting point rankings
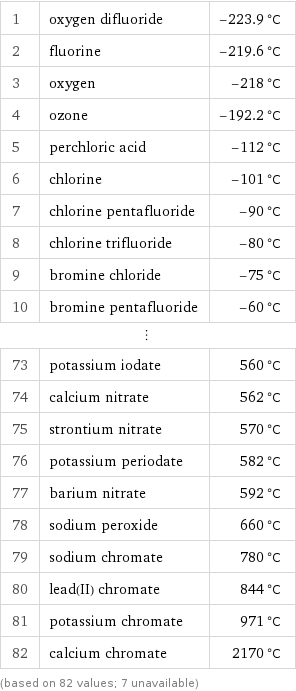
1 | oxygen difluoride | -223.9 °C 2 | fluorine | -219.6 °C 3 | oxygen | -218 °C 4 | ozone | -192.2 °C 5 | perchloric acid | -112 °C 6 | chlorine | -101 °C 7 | chlorine pentafluoride | -90 °C 8 | chlorine trifluoride | -80 °C 9 | bromine chloride | -75 °C 10 | bromine pentafluoride | -60 °C ⋮ | | 73 | potassium iodate | 560 °C 74 | calcium nitrate | 562 °C 75 | strontium nitrate | 570 °C 76 | potassium periodate | 582 °C 77 | barium nitrate | 592 °C 78 | sodium peroxide | 660 °C 79 | sodium chromate | 780 °C 80 | lead(II) chromate | 844 °C 81 | potassium chromate | 971 °C 82 | calcium chromate | 2170 °C (based on 82 values; 7 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median melting point 205 °C
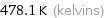
478.1 K (kelvins)
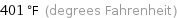
401 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)
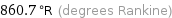
860.7 °R (degrees Rankine)
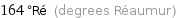
164 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)
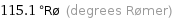
115.1 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median melting point 205 °C

27.78 °C below autoignition temperature of book paper in Ray Bradbury's famous novel (451 °F)
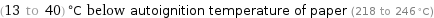
(13 to 40) °C below autoignition temperature of paper (218 to 246 °C)
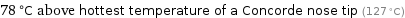
78 °C above hottest temperature of a Concorde nose tip (127 °C)
Corresponding quantities
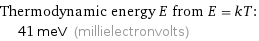
Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 41 meV (millielectronvolts)
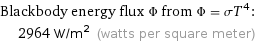
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 2964 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 2×10^-10 lx (lux)
Nearest corresponding gas marks for median melting point 205 °C (degrees Celsius)
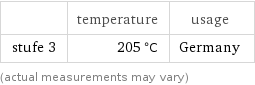
| temperature | usage stufe 3 | 205 °C | Germany (actual measurements may vary)