Input interpretation

methylamine | orbital hybridization
Result
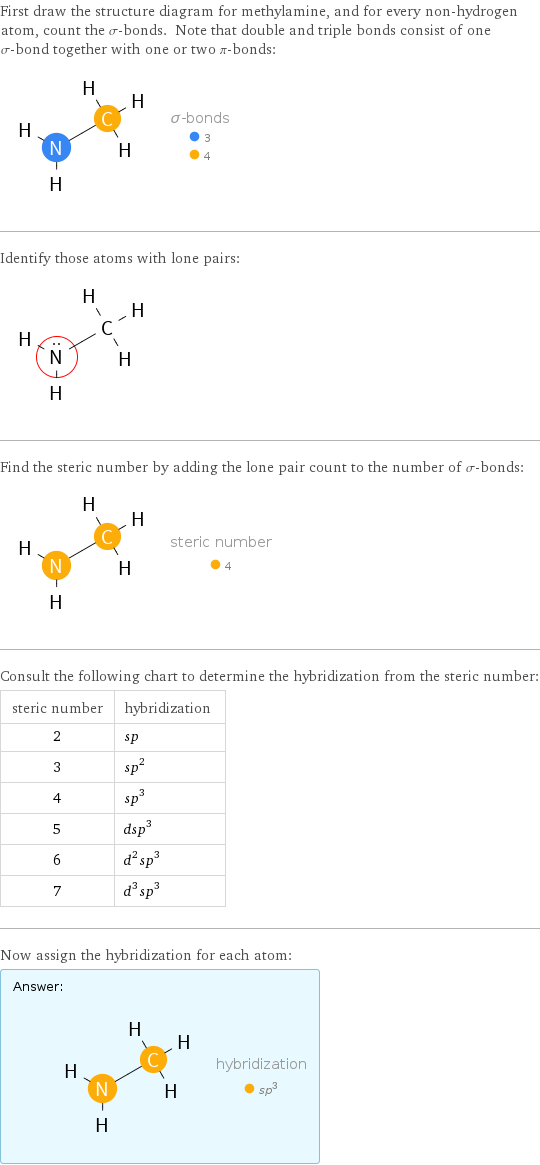
First draw the structure diagram for methylamine, and for every non-hydrogen atom, count the σ-bonds. Note that double and triple bonds consist of one σ-bond together with one or two π-bonds: Identify those atoms with lone pairs: Find the steric number by adding the lone pair count to the number of σ-bonds: Consult the following chart to determine the hybridization from the steric number: steric number | hybridization 2 | sp 3 | sp^2 4 | sp^3 5 | dsp^3 6 | d^2sp^3 7 | d^3sp^3 Now assign the hybridization for each atom: Answer: | |
Chemical names and formulas
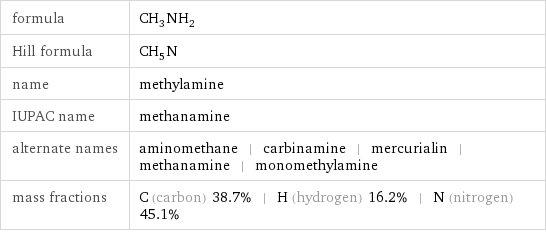
formula | CH_3NH_2 Hill formula | CH_5N name | methylamine IUPAC name | methanamine alternate names | aminomethane | carbinamine | mercurialin | methanamine | monomethylamine mass fractions | C (carbon) 38.7% | H (hydrogen) 16.2% | N (nitrogen) 45.1%