Input interpretation

succinate anion
Lewis structure
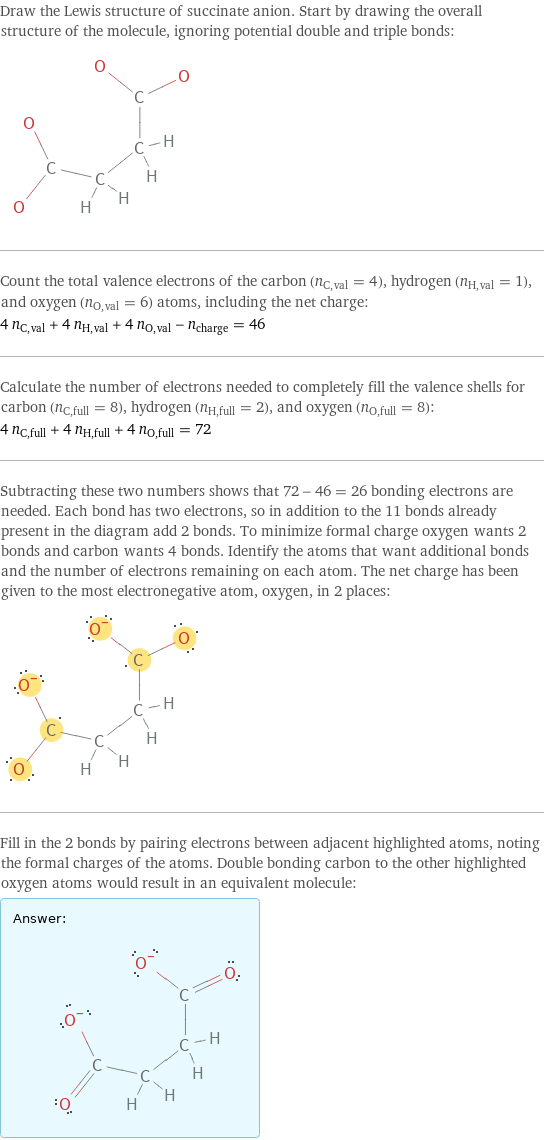
Draw the Lewis structure of succinate anion. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms, including the net charge: 4 n_C, val + 4 n_H, val + 4 n_O, val - n_charge = 46 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 4 n_C, full + 4 n_H, full + 4 n_O, full = 72 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 72 - 46 = 26 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 11 bonds already present in the diagram add 2 bonds. To minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom. The net charge has been given to the most electronegative atom, oxygen, in 2 places: Fill in the 2 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms, noting the formal charges of the atoms. Double bonding carbon to the other highlighted oxygen atoms would result in an equivalent molecule: Answer: | |
General properties
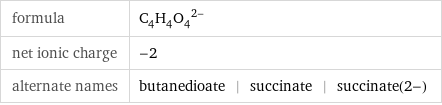
formula | (C_4H_4O_4)^(2-) net ionic charge | -2 alternate names | butanedioate | succinate | succinate(2-)
Other properties
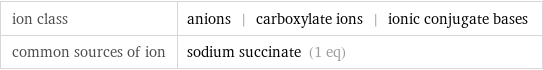
ion class | anions | carboxylate ions | ionic conjugate bases common sources of ion | sodium succinate (1 eq)