Input interpretation
nitrogen trioxide
Chemical names and formulas

formula | N_2O_3 name | nitrogen trioxide IUPAC name | nitramide alternate names | asym-dinitrogen trioxide | dinitrogen trioxide | nitrogen oxide | nitrogen oxide (2:3) mass fractions | N (nitrogen) 36.9% | O (oxygen) 63.1%
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of nitrogen trioxide. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the nitrogen (n_N, val = 5) and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 2 n_N, val + 3 n_O, val = 28 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for nitrogen (n_N, full = 8) and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 2 n_N, full + 3 n_O, full = 40 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 40 - 28 = 12 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 4 bonds already present in the diagram add 2 bonds. To minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds and nitrogen wants 3 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: To fully fill its valence shell, nitrogen will donate one of its electrons, allowing it to form four bonds (the maximum number an element on period 2 can form). Fill in the 2 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms, noting the formal charges of the atoms. Double bonding nitrogen to the other highlighted oxygen atom would result in an equivalent molecule: Answer: | |
3D structure
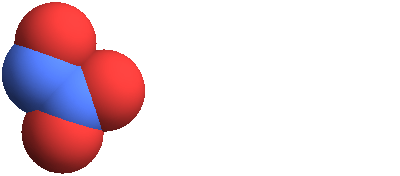
3D structure
Basic properties
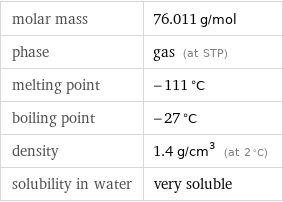
molar mass | 76.011 g/mol phase | gas (at STP) melting point | -111 °C boiling point | -27 °C density | 1.4 g/cm^3 (at 2 °C) solubility in water | very soluble
Units

Gas properties (at STP)
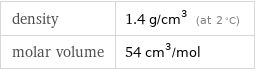
density | 1.4 g/cm^3 (at 2 °C) molar volume | 54 cm^3/mol
Units

Thermodynamic properties
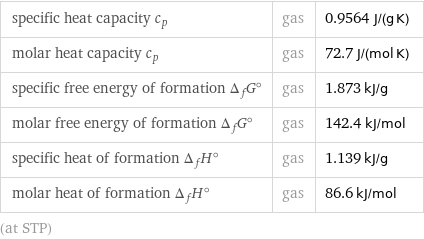
specific heat capacity c_p | gas | 0.9564 J/(g K) molar heat capacity c_p | gas | 72.7 J/(mol K) specific free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gas | 1.873 kJ/g molar free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gas | 142.4 kJ/mol specific heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | 1.139 kJ/g molar heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | 86.6 kJ/mol (at STP)
Chemical identifiers
[O-] InChI identifier | InChI=1/N2O3/c3-1-2(4)5 EU number | 234-128-5 Gmelin number | 1811](../image_source/09cae51ab24e93d7a64ccfae4fd745d4.png)
CAS number | 10544-73-7 PubChem CID number | 61526 SMILES identifier | N(=O)[N+](=O)[O-] InChI identifier | InChI=1/N2O3/c3-1-2(4)5 EU number | 234-128-5 Gmelin number | 1811
NFPA label

NFPA label
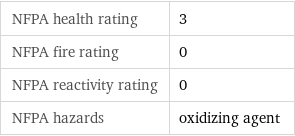
NFPA health rating | 3 NFPA fire rating | 0 NFPA reactivity rating | 0 NFPA hazards | oxidizing agent