Input interpretation
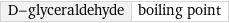
D-glyceraldehyde | boiling point
Result

228 °C (degrees Celsius)
Unit conversions
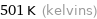
501 K (kelvins)
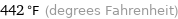
442 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)

902 °R (degrees Rankine)

182 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)
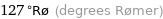
127 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparisons as temperature
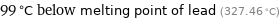
99 °C below melting point of lead (327.46 °C)

5 °C below autoignition temperature of book paper in Ray Bradbury's famous novel (451 °F)
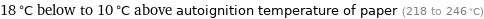
18 °C below to 10 °C above autoignition temperature of paper (218 to 246 °C)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 43 meV (millielectronvolts)
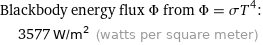
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 3577 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 1.6×10^-9 lx (lux)
Nearest corresponding gas marks
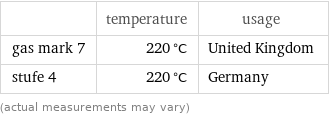
| temperature | usage gas mark 7 | 220 °C | United Kingdom stufe 4 | 220 °C | Germany (actual measurements may vary)