Input interpretation
glycerol
Chemical names and formulas
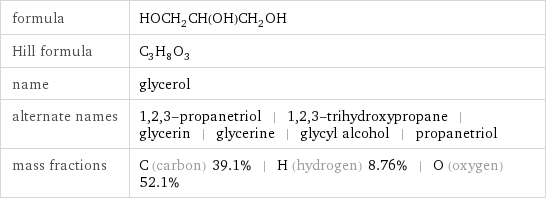
formula | HOCH_2CH(OH)CH_2OH Hill formula | C_3H_8O_3 name | glycerol alternate names | 1, 2, 3-propanetriol | 1, 2, 3-trihydroxypropane | glycerin | glycerine | glycyl alcohol | propanetriol mass fractions | C (carbon) 39.1% | H (hydrogen) 8.76% | O (oxygen) 52.1%
Lewis structure
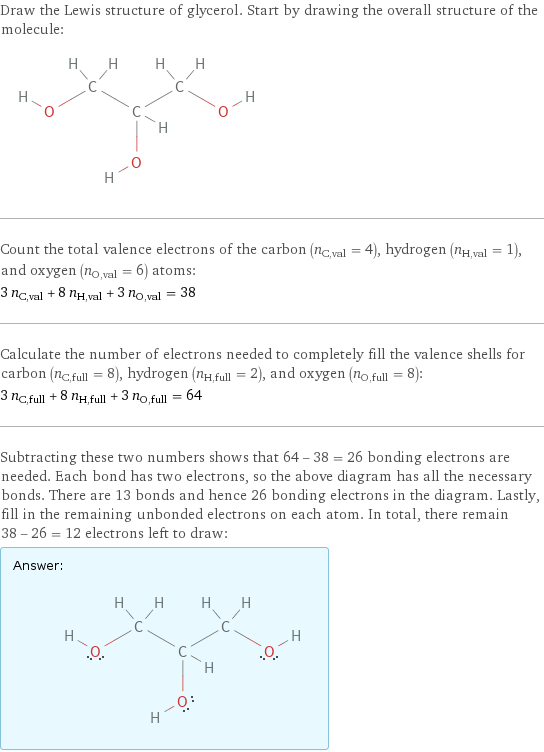
Draw the Lewis structure of glycerol. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 3 n_C, val + 8 n_H, val + 3 n_O, val = 38 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 3 n_C, full + 8 n_H, full + 3 n_O, full = 64 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 64 - 38 = 26 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. There are 13 bonds and hence 26 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 38 - 26 = 12 electrons left to draw: Answer: | |
3D structure
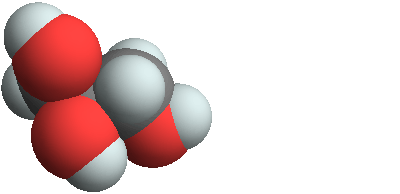
3D structure
Basic properties
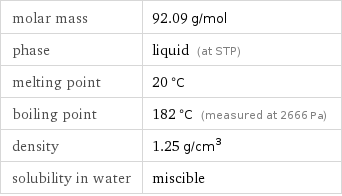
molar mass | 92.09 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) melting point | 20 °C boiling point | 182 °C (measured at 2666 Pa) density | 1.25 g/cm^3 solubility in water | miscible
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties

predicted LogP hydrophobicity | -1.92 predicted LogS | 1.1
Basic drug properties

approval status | experimental | small molecule drug categories | cryoprotective agent | solvent
Liquid properties (at STP)
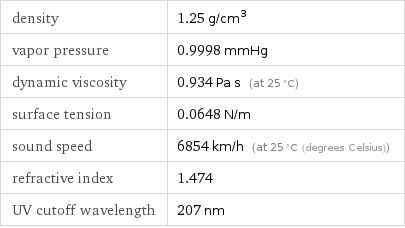
density | 1.25 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 0.9998 mmHg dynamic viscosity | 0.934 Pa s (at 25 °C) surface tension | 0.0648 N/m sound speed | 6854 km/h (at 25 °C (degrees Celsius)) refractive index | 1.474 UV cutoff wavelength | 207 nm
Units
Thermodynamic properties
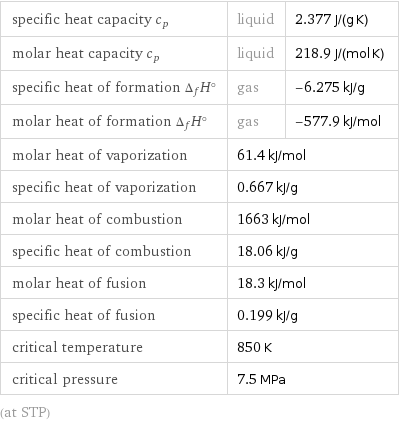
specific heat capacity c_p | liquid | 2.377 J/(g K) molar heat capacity c_p | liquid | 218.9 J/(mol K) specific heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | -6.275 kJ/g molar heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | -577.9 kJ/mol molar heat of vaporization | 61.4 kJ/mol | specific heat of vaporization | 0.667 kJ/g | molar heat of combustion | 1663 kJ/mol | specific heat of combustion | 18.06 kJ/g | molar heat of fusion | 18.3 kJ/mol | specific heat of fusion | 0.199 kJ/g | critical temperature | 850 K | critical pressure | 7.5 MPa | (at STP)
Chemical identifiers

CAS number | 56-81-5 Beilstein number | 635685 PubChem CID number | 753 PubChem SID number | 7886777 SMILES identifier | C(C(CO)O)O InChI identifier | InChI=1/C3H8O3/c4-1-3(6)2-5/h3-6H, 1-2H2 InChI key | PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYAF RTECS number | MA8050000 MDL number | MFCD00004722
NFPA label

NFPA label
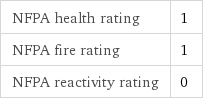
NFPA health rating | 1 NFPA fire rating | 1 NFPA reactivity rating | 0
Safety properties
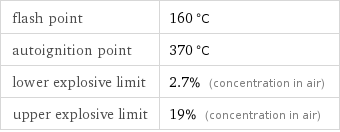
flash point | 160 °C autoignition point | 370 °C lower explosive limit | 2.7% (concentration in air) upper explosive limit | 19% (concentration in air)
Toxicity properties
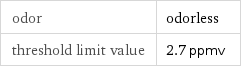
odor | odorless threshold limit value | 2.7 ppmv

RTECS classes | drug | mutagen | reproductive effector | human data | primary irritant