Input interpretation
doxylamine
Chemical names and formulas
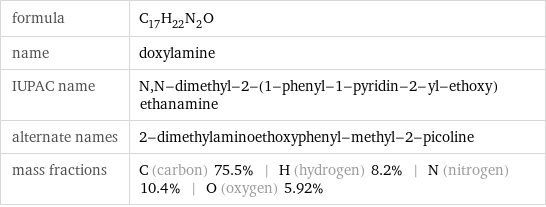
formula | C_17H_22N_2O name | doxylamine IUPAC name | N, N-dimethyl-2-(1-phenyl-1-pyridin-2-yl-ethoxy)ethanamine alternate names | 2-dimethylaminoethoxyphenyl-methyl-2-picoline mass fractions | C (carbon) 75.5% | H (hydrogen) 8.2% | N (nitrogen) 10.4% | O (oxygen) 5.92%
Lewis structure
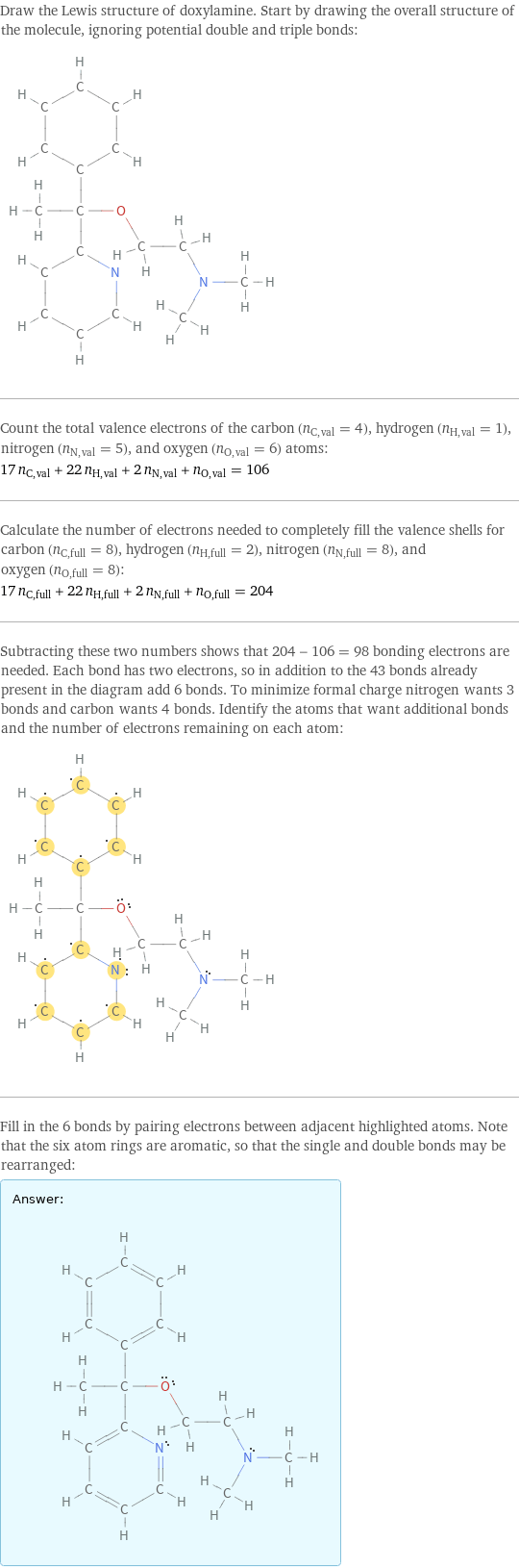
Draw the Lewis structure of doxylamine. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 17 n_C, val + 22 n_H, val + 2 n_N, val + n_O, val = 106 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 17 n_C, full + 22 n_H, full + 2 n_N, full + n_O, full = 204 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 204 - 106 = 98 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 43 bonds already present in the diagram add 6 bonds. To minimize formal charge nitrogen wants 3 bonds and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 6 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms. Note that the six atom rings are aromatic, so that the single and double bonds may be rearranged: Answer: | |
3D structure
3D structure
Basic properties
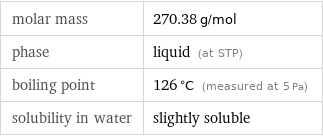
molar mass | 270.38 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) boiling point | 126 °C (measured at 5 Pa) solubility in water | slightly soluble
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties

experimental LogP hydrophobicity | 2.5 predicted LogP hydrophobicity | 2.9 predicted LogS | -2.7
Basic drug properties

approval status | approved | small molecule drug categories | anti-allergic agent | antiemetic | antitussive agent | histamine h1 antagonist | hypnotics and sedative dosage forms | oral: tablet
Liquid properties (at STP)

refractive index | 1.5804
Chemical identifiers

CAS number | 469-21-6 Beilstein number | 230379 PubChem CID number | 3162 PubChem SID number | 7979131 SMILES identifier | CC(C1=CC=CC=C1)(C2=CC=CC=N2)OCCN(C)C InChI identifier | InChI=1/C17H22N2O/c1-17(20-14-13-19(2)3, 15-9-5-4-6-10-15)16-11-7-8-12-18-16/h4-12H, 13-14H2, 1-3H3 InChI key | HCFDWZZGGLSKEP-UHFFFAOYAC EU number | 207-414-2 RTECS number | US9250000
Toxicity properties

RTECS classes | drug | human data