Input interpretation
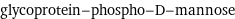
glycoprotein-phospho-D-mannose
Chemical names and formulas

formula | C_34H_58N_5O_26P_1 Hill formula | C_34H_58N_5O_26P name | glycoprotein-phospho-D-mannose mass fractions | C (carbon) 41.6% | H (hydrogen) 5.75% | N (nitrogen) 7.13% | O (oxygen) 42.4% | P (phosphorus) 3.15%
Lewis structure
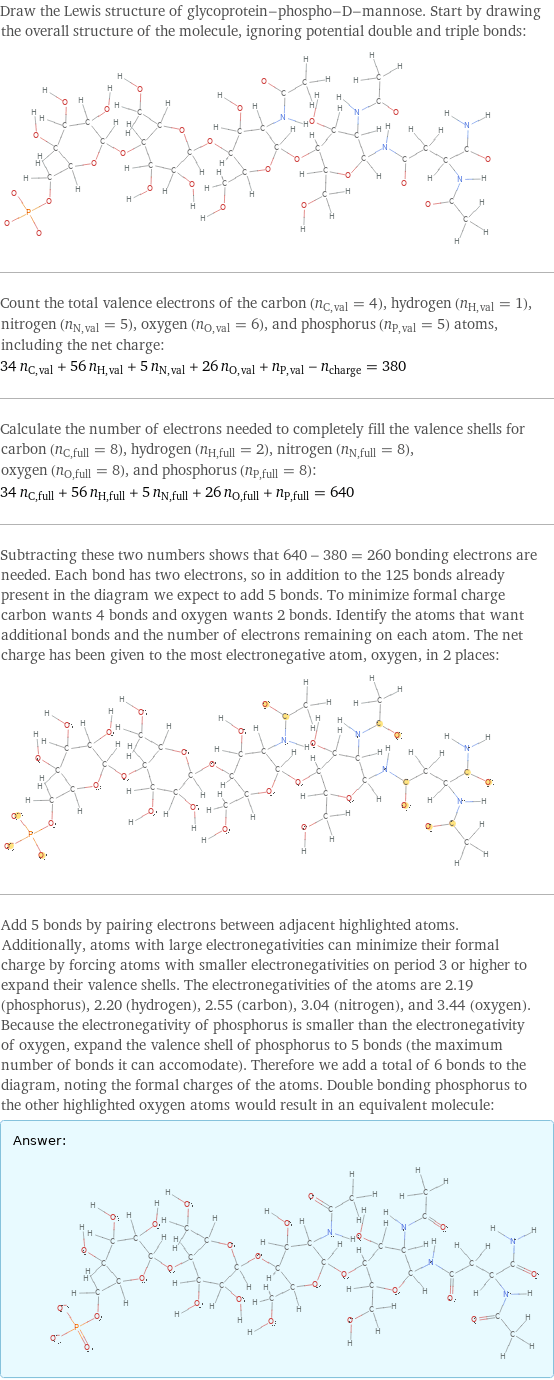
Draw the Lewis structure of glycoprotein-phospho-D-mannose. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), oxygen (n_O, val = 6), and phosphorus (n_P, val = 5) atoms, including the net charge: 34 n_C, val + 56 n_H, val + 5 n_N, val + 26 n_O, val + n_P, val - n_charge = 380 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), oxygen (n_O, full = 8), and phosphorus (n_P, full = 8): 34 n_C, full + 56 n_H, full + 5 n_N, full + 26 n_O, full + n_P, full = 640 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 640 - 380 = 260 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 125 bonds already present in the diagram we expect to add 5 bonds. To minimize formal charge carbon wants 4 bonds and oxygen wants 2 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom. The net charge has been given to the most electronegative atom, oxygen, in 2 places: Add 5 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms. Additionally, atoms with large electronegativities can minimize their formal charge by forcing atoms with smaller electronegativities on period 3 or higher to expand their valence shells. The electronegativities of the atoms are 2.19 (phosphorus), 2.20 (hydrogen), 2.55 (carbon), 3.04 (nitrogen), and 3.44 (oxygen). Because the electronegativity of phosphorus is smaller than the electronegativity of oxygen, expand the valence shell of phosphorus to 5 bonds (the maximum number of bonds it can accomodate). Therefore we add a total of 6 bonds to the diagram, noting the formal charges of the atoms. Double bonding phosphorus to the other highlighted oxygen atoms would result in an equivalent molecule: Answer: | |
Basic properties

molar mass | 981.8 g/mol
Units

Chemical identifiers
![PubChem CID number | 25201868 SMILES identifier | CC(=O)NC(CC(=O)NC4(OC(CO)C(OC3(OC(CO)C(OC2(OC(CO)C(OC1(OC(COP(=O)([O-])[O-])C(O)C(O)C(O)1))C(O)C(O)2))C(O)C(NC(C)=O)3))C(O)C(NC(C)=O)4))C(N)=O](../image_source/27e0c346ffa5ceda9d35ac63845afa16.png)
PubChem CID number | 25201868 SMILES identifier | CC(=O)NC(CC(=O)NC4(OC(CO)C(OC3(OC(CO)C(OC2(OC(CO)C(OC1(OC(COP(=O)([O-])[O-])C(O)C(O)C(O)1))C(O)C(O)2))C(O)C(NC(C)=O)3))C(O)C(NC(C)=O)4))C(N)=O