Input interpretation
carbon disulfide
Chemical names and formulas

formula | CS_2 name | carbon disulfide IUPAC name | methanedithione alternate names | carbon bisulfide | carbon bisulphide | carbon disulphide | carbon sulfide | methanedithione | weeviltox mass fractions | C (carbon) 15.8% | S (sulfur) 84.2%
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of carbon disulfide. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4) and sulfur (n_S, val = 6) atoms: n_C, val + 2 n_S, val = 16 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8) and sulfur (n_S, full = 8): n_C, full + 2 n_S, full = 24 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 24 - 16 = 8 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 2 bonds already present in the diagram add 2 bonds. To minimize formal charge sulfur wants 2 bonds and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 2 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms: Answer: | |
3D structure

3D structure
Basic properties
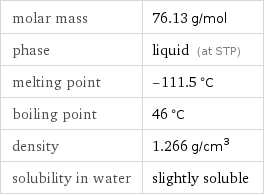
molar mass | 76.13 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) melting point | -111.5 °C boiling point | 46 °C density | 1.266 g/cm^3 solubility in water | slightly soluble
Units

Liquid properties (at STP)
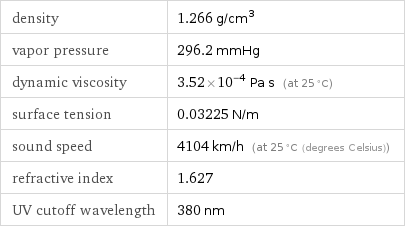
density | 1.266 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 296.2 mmHg dynamic viscosity | 3.52×10^-4 Pa s (at 25 °C) surface tension | 0.03225 N/m sound speed | 4104 km/h (at 25 °C (degrees Celsius)) refractive index | 1.627 UV cutoff wavelength | 380 nm
Units
Thermodynamic properties
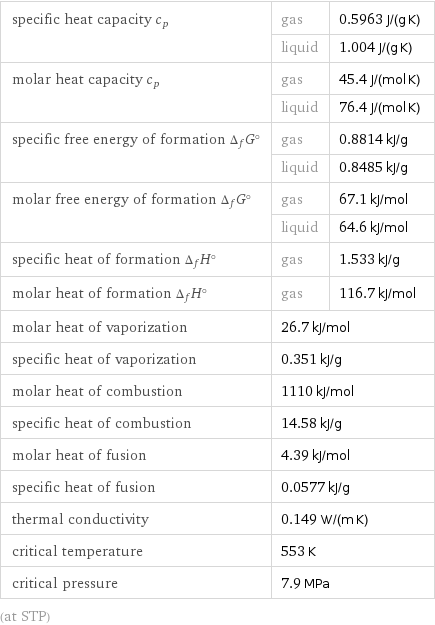
specific heat capacity c_p | gas | 0.5963 J/(g K) | liquid | 1.004 J/(g K) molar heat capacity c_p | gas | 45.4 J/(mol K) | liquid | 76.4 J/(mol K) specific free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gas | 0.8814 kJ/g | liquid | 0.8485 kJ/g molar free energy of formation Δ_fG° | gas | 67.1 kJ/mol | liquid | 64.6 kJ/mol specific heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | 1.533 kJ/g molar heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | 116.7 kJ/mol molar heat of vaporization | 26.7 kJ/mol | specific heat of vaporization | 0.351 kJ/g | molar heat of combustion | 1110 kJ/mol | specific heat of combustion | 14.58 kJ/g | molar heat of fusion | 4.39 kJ/mol | specific heat of fusion | 0.0577 kJ/g | thermal conductivity | 0.149 W/(m K) | critical temperature | 553 K | critical pressure | 7.9 MPa | (at STP)
Chemical identifiers
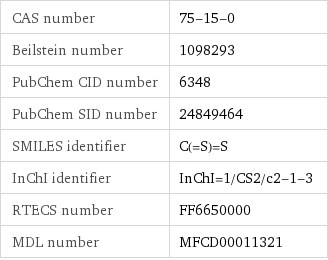
CAS number | 75-15-0 Beilstein number | 1098293 PubChem CID number | 6348 PubChem SID number | 24849464 SMILES identifier | C(=S)=S InChI identifier | InChI=1/CS2/c2-1-3 RTECS number | FF6650000 MDL number | MFCD00011321
NFPA label

NFPA label
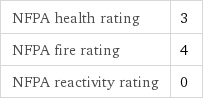
NFPA health rating | 3 NFPA fire rating | 4 NFPA reactivity rating | 0
Safety properties
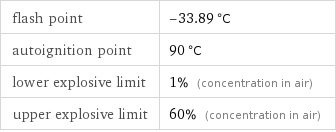
flash point | -33.89 °C autoignition point | 90 °C lower explosive limit | 1% (concentration in air) upper explosive limit | 60% (concentration in air)
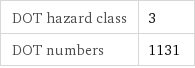
DOT hazard class | 3 DOT numbers | 1131
Toxicity properties
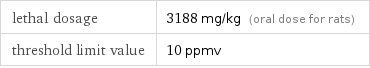
lethal dosage | 3188 mg/kg (oral dose for rats) threshold limit value | 10 ppmv
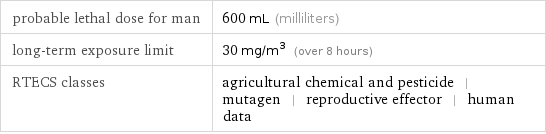
probable lethal dose for man | 600 mL (milliliters) long-term exposure limit | 30 mg/m^3 (over 8 hours) RTECS classes | agricultural chemical and pesticide | mutagen | reproductive effector | human data