Input interpretation

Poiseuille's law
Equation
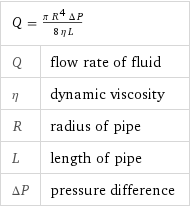
Q = (π R^4 ΔP)/(8 η L) | Q | flow rate of fluid η | dynamic viscosity R | radius of pipe L | length of pipe ΔP | pressure difference
Input values
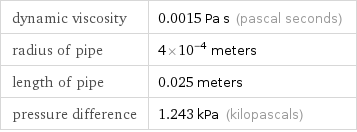
dynamic viscosity | 0.0015 Pa s (pascal seconds) radius of pipe | 4×10^-4 meters length of pipe | 0.025 meters pressure difference | 1.243 kPa (kilopascals)
Results

flow rate of fluid | 0.333 mL/s (milliliters per second) = 0.317 gal/h (gallons per hour) = 2780 gal/yr (gallons per year) = 20 mL/min (milliliters per minute) = 0.02 L/min (liters per minute) = 1200 mL/h (milliliters per hour) = 28.8 L/day (liters per day) = 20 cm^3/min (cubic centimeters per minute)
Possible intermediate steps

Calculate the flow rate of fluid using the following information: known variables | | η | dynamic viscosity | 0.0015 Pa s R | radius of pipe | 4×10^-4 m L | length of pipe | 0.025 m ΔP | pressure difference | 1.243 kPa Convert known variables into appropriate units using the following: 1 Pa s = 1000 g/(m s): 1 kPa = 1×10^6 g/(m s^2): known variables | | η | dynamic viscosity | 1.5 g/(m s) R | radius of pipe | 4×10^-4 m L | length of pipe | 0.025 m ΔP | pressure difference | 1.243×10^6 g/(m s^2) The relevant equation that relates flow rate of fluid (Q), dynamic viscosity (η), radius of pipe (R), length of pipe (L), and pressure difference (ΔP) is: Q = (π R^4 ΔP)/(8 η L) Substitute known variables and constants into the equation: known variables | | η | dynamic viscosity | 1.5 g/(m s) R | radius of pipe | 4×10^-4 m L | length of pipe | 0.025 m ΔP | pressure difference | 1.243×10^6 g/(m s^2) constant | | π | pi | 3.1416 | : Q = (3.1416 (4×10^-4 m)^4×1.243×10^6 g/(m s^2))/(8×1.5 g/(m s)×0.025 m) Separate the numerical part, (3.1416 (4×10^-4)^4×1.243×10^6)/(8×1.5×0.025), from the unit part, (m^4×g/(m s^2))/(g/(m s) m) = m^3/s: Q = (3.1416 (4×10^-4)^4×1.243×10^6)/(8×1.5×0.025) m^3/s Evaluate (3.1416 (4×10^-4)^4×1.243×10^6)/(8×1.5×0.025): Q = 3.332×10^-7 m^3/s Convert 3.332×10^-7 m^3/s into mL/s (milliliters per second) using the following: 1 m^3/s = 1×10^6 mL/s: Answer: | | Q = 0.333 mL/s