Input interpretation
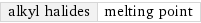
alkyl halides | melting point
Summary
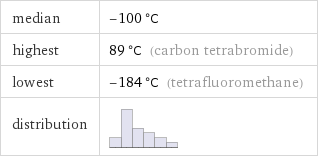
median | -100 °C highest | 89 °C (carbon tetrabromide) lowest | -184 °C (tetrafluoromethane) distribution |
Distribution plots
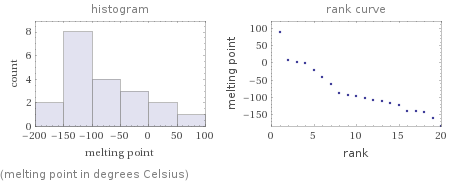
(melting point in degrees Celsius)
Melting point rankings
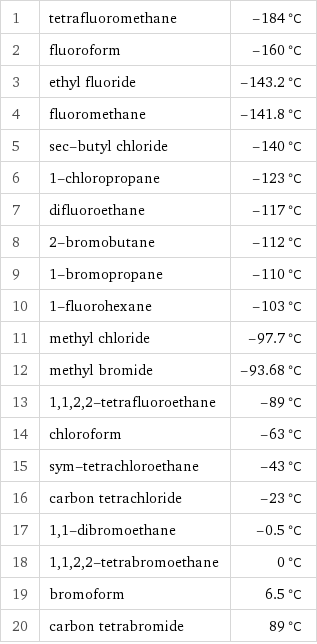
1 | tetrafluoromethane | -184 °C 2 | fluoroform | -160 °C 3 | ethyl fluoride | -143.2 °C 4 | fluoromethane | -141.8 °C 5 | sec-butyl chloride | -140 °C 6 | 1-chloropropane | -123 °C 7 | difluoroethane | -117 °C 8 | 2-bromobutane | -112 °C 9 | 1-bromopropane | -110 °C 10 | 1-fluorohexane | -103 °C 11 | methyl chloride | -97.7 °C 12 | methyl bromide | -93.68 °C 13 | 1, 1, 2, 2-tetrafluoroethane | -89 °C 14 | chloroform | -63 °C 15 | sym-tetrachloroethane | -43 °C 16 | carbon tetrachloride | -23 °C 17 | 1, 1-dibromoethane | -0.5 °C 18 | 1, 1, 2, 2-tetrabromoethane | 0 °C 19 | bromoform | 6.5 °C 20 | carbon tetrabromide | 89 °C
Unit conversions for median melting point -100 °C
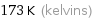
173 K (kelvins)
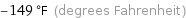
-149 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)

311 °R (degrees Rankine)

-80.3 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)
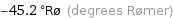
-45.2 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median melting point -100 °C
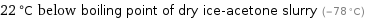
22 °C below boiling point of dry ice-acetone slurry (-78 °C)
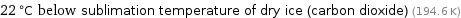
22 °C below sublimation temperature of dry ice (carbon dioxide) (194.6 K)
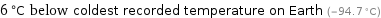
6 °C below coldest recorded temperature on Earth (-94.7 °C)
Corresponding quantities
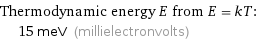
Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 15 meV (millielectronvolts)
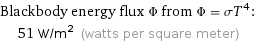
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 51 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 7.8×10^-42 lx (lux)