Input interpretation
cyclosporin A
Chemical names and formulas
![formula | C_62H_111N_11O_12 name | cyclosporin A IUPAC name | 30-ethyl-33-[(E, 1S, 2S)-1-hydroxy-2-methyl-hex-4-enyl]-1, 4, 7, 10, 12, 15, 19, 25, 28-nonamethyl-6, 9, 18, 24-tetrakis(2-methylpropyl)-3, 21-dipropan-2-yl-1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19, 22, 25, 28, 31-undecazacyclotritriacontane-2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23, 26, 29, 32-undecone alternate names | cipol n | sandimmune mass fractions | C (carbon) 61.9% | H (hydrogen) 9.3% | N (nitrogen) 12.8% | O (oxygen) 16%](../image_source/51ecf5fc5c341e2b034af0fa3396e537.png)
formula | C_62H_111N_11O_12 name | cyclosporin A IUPAC name | 30-ethyl-33-[(E, 1S, 2S)-1-hydroxy-2-methyl-hex-4-enyl]-1, 4, 7, 10, 12, 15, 19, 25, 28-nonamethyl-6, 9, 18, 24-tetrakis(2-methylpropyl)-3, 21-dipropan-2-yl-1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19, 22, 25, 28, 31-undecazacyclotritriacontane-2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23, 26, 29, 32-undecone alternate names | cipol n | sandimmune mass fractions | C (carbon) 61.9% | H (hydrogen) 9.3% | N (nitrogen) 12.8% | O (oxygen) 16%
Lewis structure
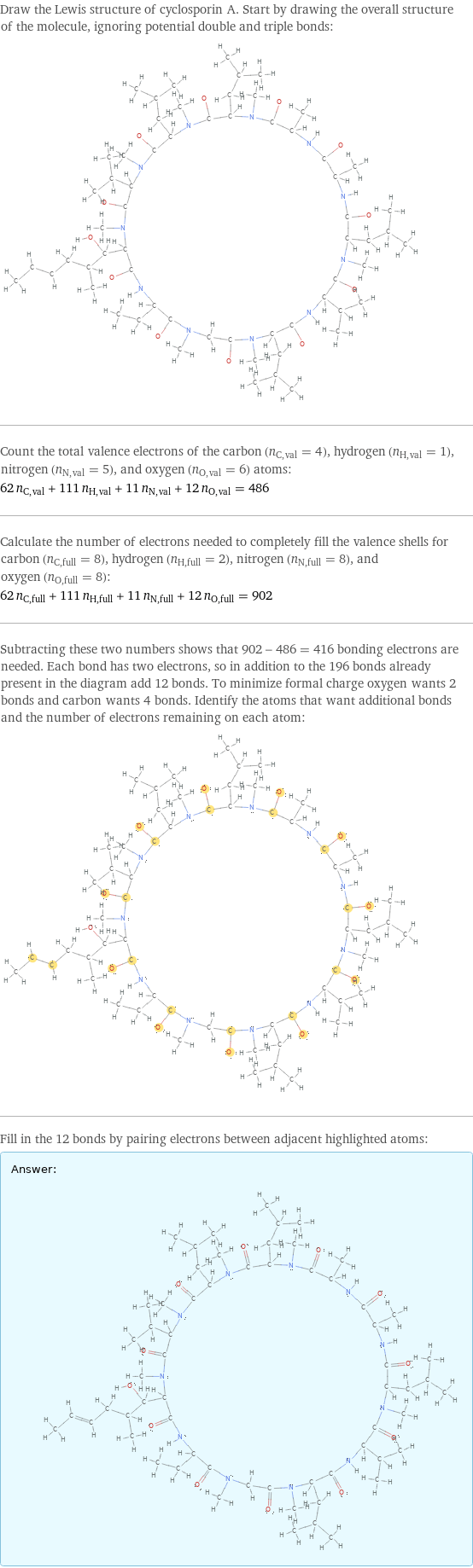
Draw the Lewis structure of cyclosporin A. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4), hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), nitrogen (n_N, val = 5), and oxygen (n_O, val = 6) atoms: 62 n_C, val + 111 n_H, val + 11 n_N, val + 12 n_O, val = 486 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8), hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), nitrogen (n_N, full = 8), and oxygen (n_O, full = 8): 62 n_C, full + 111 n_H, full + 11 n_N, full + 12 n_O, full = 902 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 902 - 486 = 416 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 196 bonds already present in the diagram add 12 bonds. To minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds and carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 12 bonds by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms: Answer: | |
3D structure
3D structure
Basic properties
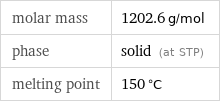
molar mass | 1202.6 g/mol phase | solid (at STP) melting point | 150 °C
Units

Hydrophobicity and permeability properties
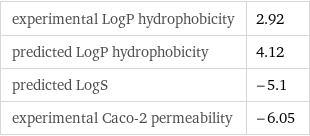
experimental LogP hydrophobicity | 2.92 predicted LogP hydrophobicity | 4.12 predicted LogS | -5.1 experimental Caco-2 permeability | -6.05
Drug interactions

acetazolamide | allopurinol | amiodarone | amobarbital | amphotericin b | amprenavir | allylpropymal | atazanavir | atorvastatin | azithromycin | bosentan | bupropion | butabarbital | butalbital | butethal | carbamazepine | carvedilol | caspofungin | cerivastatin | chloramphenicol | ... (total: 131)
Basic drug properties
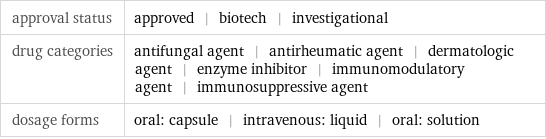
approval status | approved | biotech | investigational drug categories | antifungal agent | antirheumatic agent | dermatologic agent | enzyme inhibitor | immunomodulatory agent | immunosuppressive agent dosage forms | oral: capsule | intravenous: liquid | oral: solution

brand names | gengraf (abbott labs) | neoral (novartis) | restasis | restasis (allergan inc) | sandimmune (novartis) | sangcya
Chemical identifiers

CAS number | 59865-13-3 Beilstein number | 3586327 PubChem CID number | 5458585 PubChem SID number | 199551 SMILES identifier | CCC1C(=O)N(CC(=O)N(C(C(=O)NC(C(=O)N(C(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)N(C(C(=O)N(C(C(=O)N(C(C(=O)N(C(C(=O)N1)C(C(C)CC=CC)O)C)C(C)C)C)CC(C)C)C)CC(C)C)C)C)C)CC(C)C)C)C(C)C)CC(C)C)C)C InChI identifier | InChI=1/C62H111N11O12/c1-25-27-28-40(15)52(75)51-56(79)65-43(26-2)58(81)67(18)33-48(74)68(19)44(29-34(3)4)55(78)66-49(38(11)12)61(84)69(20)45(30-35(5)6)54(77)63-41(16)53(76)64-42(17)57(80)70(21)46(31-36(7)8)59(82)71(22)47(32-37(9)10)60(83)72(23)50(39(13)14)62(85)73(51)24/h25, 27, 34-47, 49-52, 75H, 26, 28-33H2, 1-24H3, (H, 63, 77)(H, 64, 76)(H, 65, 79)(H, 66, 78)/b27-25+/t40-, 41u, 42u, 43u, 44u, 45u, 46u, 47u, 49u, 50u, 51?, 52-/m0/s1/f/h63-66H InChI key | PMATZTZNYRCHOR-CCMIHKRJDW RTECS number | GZ4120000 NSC number | 290193
Toxicity properties

RTECS classes | tumorigen | drug | mutagen | reproductive effector | human data