Input interpretation
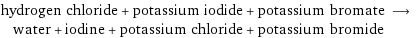
hydrogen chloride + potassium iodide + potassium bromate ⟶ water + iodine + potassium chloride + potassium bromide
Balanced equation

Balance the chemical equation algebraically: + + ⟶ + + + Add stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, to the reactants and products: c_1 + c_2 + c_3 ⟶ c_4 + c_5 + c_6 + c_7 Set the number of atoms in the reactants equal to the number of atoms in the products for Cl, H, I, K, Br and O: Cl: | c_1 = c_6 H: | c_1 = 2 c_4 I: | c_2 = 2 c_5 K: | c_2 + c_3 = c_6 + c_7 Br: | c_3 = c_7 O: | 3 c_3 = c_4 Since the coefficients are relative quantities and underdetermined, choose a coefficient to set arbitrarily. To keep the coefficients small, the arbitrary value is ordinarily one. For instance, set c_3 = 1 and solve the system of equations for the remaining coefficients: c_1 = 6 c_2 = 6 c_3 = 1 c_4 = 3 c_5 = 3 c_6 = 6 c_7 = 1 Substitute the coefficients into the chemical reaction to obtain the balanced equation: Answer: | | 6 + 6 + ⟶ 3 + 3 + 6 +
Structures
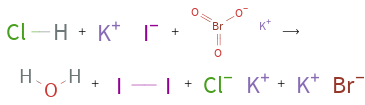
+ + ⟶ + + +
Names
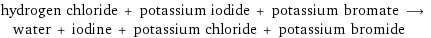
hydrogen chloride + potassium iodide + potassium bromate ⟶ water + iodine + potassium chloride + potassium bromide
Reaction thermodynamics
Enthalpy
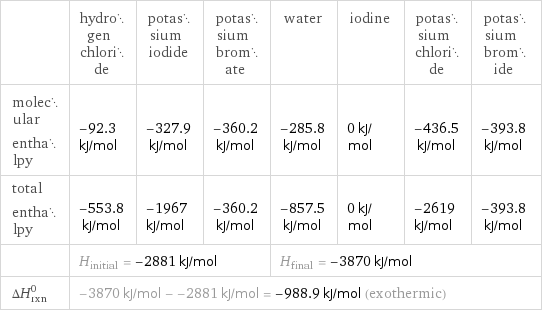
| hydrogen chloride | potassium iodide | potassium bromate | water | iodine | potassium chloride | potassium bromide molecular enthalpy | -92.3 kJ/mol | -327.9 kJ/mol | -360.2 kJ/mol | -285.8 kJ/mol | 0 kJ/mol | -436.5 kJ/mol | -393.8 kJ/mol total enthalpy | -553.8 kJ/mol | -1967 kJ/mol | -360.2 kJ/mol | -857.5 kJ/mol | 0 kJ/mol | -2619 kJ/mol | -393.8 kJ/mol | H_initial = -2881 kJ/mol | | | H_final = -3870 kJ/mol | | | ΔH_rxn^0 | -3870 kJ/mol - -2881 kJ/mol = -988.9 kJ/mol (exothermic) | | | | | |
Gibbs free energy
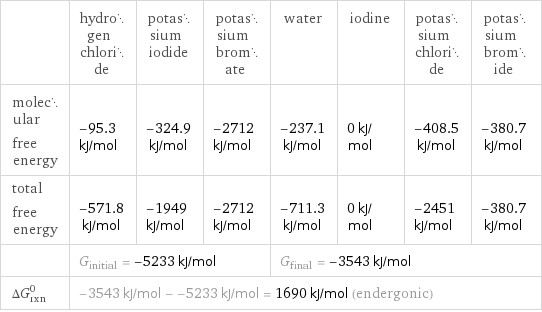
| hydrogen chloride | potassium iodide | potassium bromate | water | iodine | potassium chloride | potassium bromide molecular free energy | -95.3 kJ/mol | -324.9 kJ/mol | -2712 kJ/mol | -237.1 kJ/mol | 0 kJ/mol | -408.5 kJ/mol | -380.7 kJ/mol total free energy | -571.8 kJ/mol | -1949 kJ/mol | -2712 kJ/mol | -711.3 kJ/mol | 0 kJ/mol | -2451 kJ/mol | -380.7 kJ/mol | G_initial = -5233 kJ/mol | | | G_final = -3543 kJ/mol | | | ΔG_rxn^0 | -3543 kJ/mol - -5233 kJ/mol = 1690 kJ/mol (endergonic) | | | | | |
Equilibrium constant
![K_c = ([H2O]^3 [I2]^3 [KCl]^6 [KBr])/([HCl]^6 [KI]^6 [KBrO3])](../image_source/25bd17e777725910158df098cb17ab09.png)
K_c = ([H2O]^3 [I2]^3 [KCl]^6 [KBr])/([HCl]^6 [KI]^6 [KBrO3])
Rate of reaction
![rate = -1/6 (Δ[HCl])/(Δt) = -1/6 (Δ[KI])/(Δt) = -(Δ[KBrO3])/(Δt) = 1/3 (Δ[H2O])/(Δt) = 1/3 (Δ[I2])/(Δt) = 1/6 (Δ[KCl])/(Δt) = (Δ[KBr])/(Δt) (assuming constant volume and no accumulation of intermediates or side products)](../image_source/2a39596257a273c4085947b4debf84be.png)
rate = -1/6 (Δ[HCl])/(Δt) = -1/6 (Δ[KI])/(Δt) = -(Δ[KBrO3])/(Δt) = 1/3 (Δ[H2O])/(Δt) = 1/3 (Δ[I2])/(Δt) = 1/6 (Δ[KCl])/(Δt) = (Δ[KBr])/(Δt) (assuming constant volume and no accumulation of intermediates or side products)
Chemical names and formulas
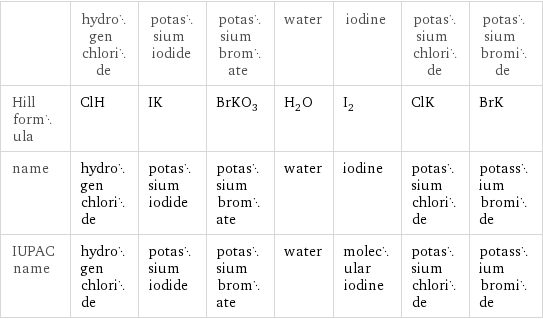
| hydrogen chloride | potassium iodide | potassium bromate | water | iodine | potassium chloride | potassium bromide Hill formula | ClH | IK | BrKO_3 | H_2O | I_2 | ClK | BrK name | hydrogen chloride | potassium iodide | potassium bromate | water | iodine | potassium chloride | potassium bromide IUPAC name | hydrogen chloride | potassium iodide | potassium bromate | water | molecular iodine | potassium chloride | potassium bromide