Input interpretation
trans-2-butene
Chemical names and formulas
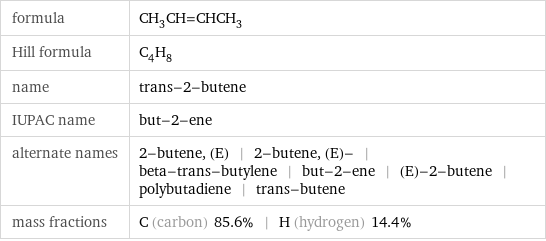
formula | CH_3CH=CHCH_3 Hill formula | C_4H_8 name | trans-2-butene IUPAC name | but-2-ene alternate names | 2-butene, (E) | 2-butene, (E)- | beta-trans-butylene | but-2-ene | (E)-2-butene | polybutadiene | trans-butene mass fractions | C (carbon) 85.6% | H (hydrogen) 14.4%
Lewis structure
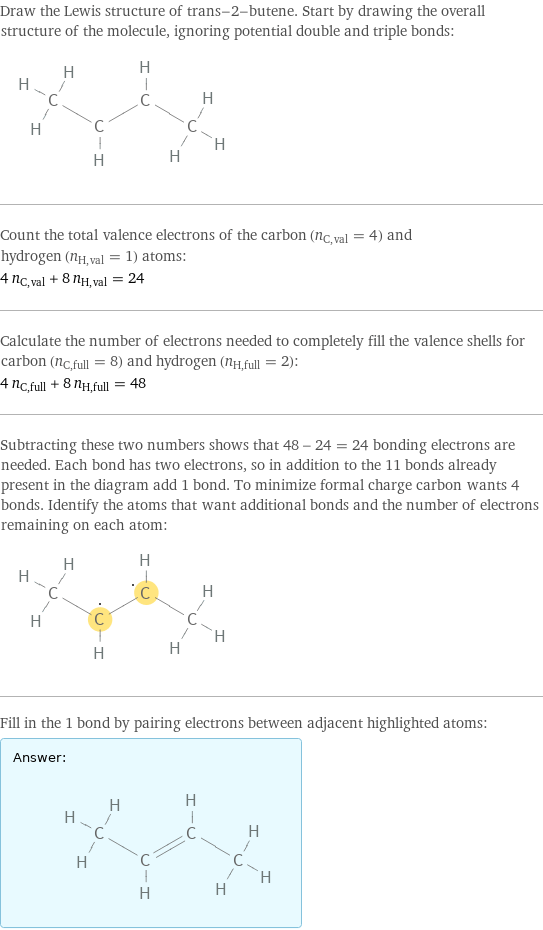
Draw the Lewis structure of trans-2-butene. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the carbon (n_C, val = 4) and hydrogen (n_H, val = 1) atoms: 4 n_C, val + 8 n_H, val = 24 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for carbon (n_C, full = 8) and hydrogen (n_H, full = 2): 4 n_C, full + 8 n_H, full = 48 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 48 - 24 = 24 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so in addition to the 11 bonds already present in the diagram add 1 bond. To minimize formal charge carbon wants 4 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: Fill in the 1 bond by pairing electrons between adjacent highlighted atoms: Answer: | |
3D structure
3D structure
Basic properties
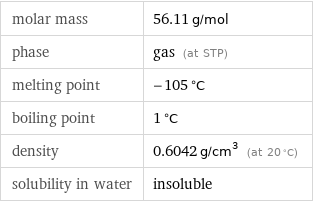
molar mass | 56.11 g/mol phase | gas (at STP) melting point | -105 °C boiling point | 1 °C density | 0.6042 g/cm^3 (at 20 °C) solubility in water | insoluble
Units

Gas properties (at STP)
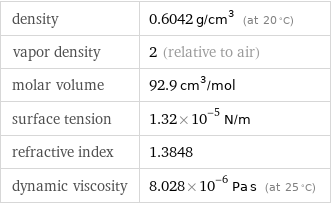
density | 0.6042 g/cm^3 (at 20 °C) vapor density | 2 (relative to air) molar volume | 92.9 cm^3/mol surface tension | 1.32×10^-5 N/m refractive index | 1.3848 dynamic viscosity | 8.028×10^-6 Pa s (at 25 °C)
Units

Thermodynamic properties
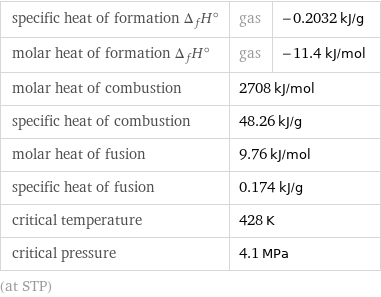
specific heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | -0.2032 kJ/g molar heat of formation Δ_fH° | gas | -11.4 kJ/mol molar heat of combustion | 2708 kJ/mol | specific heat of combustion | 48.26 kJ/g | molar heat of fusion | 9.76 kJ/mol | specific heat of fusion | 0.174 kJ/g | critical temperature | 428 K | critical pressure | 4.1 MPa | (at STP)
Phase diagram
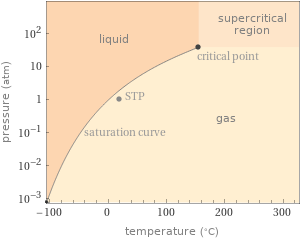
Phase diagram
Units

Chemical identifiers
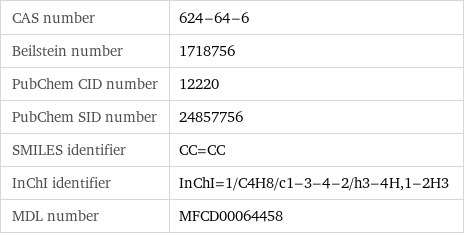
CAS number | 624-64-6 Beilstein number | 1718756 PubChem CID number | 12220 PubChem SID number | 24857756 SMILES identifier | CC=CC InChI identifier | InChI=1/C4H8/c1-3-4-2/h3-4H, 1-2H3 MDL number | MFCD00064458
NFPA label

NFPA label

NFPA health rating | 2 NFPA fire rating | 4 NFPA reactivity rating | 1
Safety properties
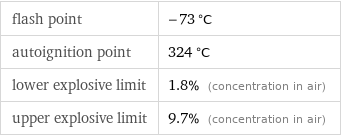
flash point | -73 °C autoignition point | 324 °C lower explosive limit | 1.8% (concentration in air) upper explosive limit | 9.7% (concentration in air)

DOT hazard class | 2.1 DOT numbers | 1012