Input interpretation

period 4 elements | superconducting point
Summary

median | 0.85 K highest | 5.4 K (vanadium) lowest | 0.05 K (scandium) | (based on 5 values; 13 unavailable)
Entities with missing values
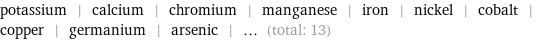
potassium | calcium | chromium | manganese | iron | nickel | cobalt | copper | germanium | arsenic | ... (total: 13)
Superconducting point rankings
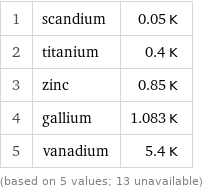
1 | scandium | 0.05 K 2 | titanium | 0.4 K 3 | zinc | 0.85 K 4 | gallium | 1.083 K 5 | vanadium | 5.4 K (based on 5 values; 13 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median superconducting point 0.85 K

-272.3 °C (degrees Celsius)

-458.1 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)

1.5 °R (degrees Rankine)

-217.84 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)

-135.5 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median superconducting point 0.85 K
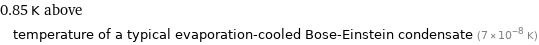
0.85 K above temperature of a typical evaporation-cooled Bose-Einstein condensate (7×10^-8 K)

0.85 K above lowest temperature sodium Bose-Einstein condensate gas ever achieved in the laboratory (at MIT) (450 pK)

0.85 K above absolute zero (0 K)
Corresponding quantity
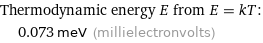
Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 0.073 meV (millielectronvolts)