Input interpretation
arsenic (chemical element) | antimony (chemical element) | fermium (chemical element)
Periodic table location
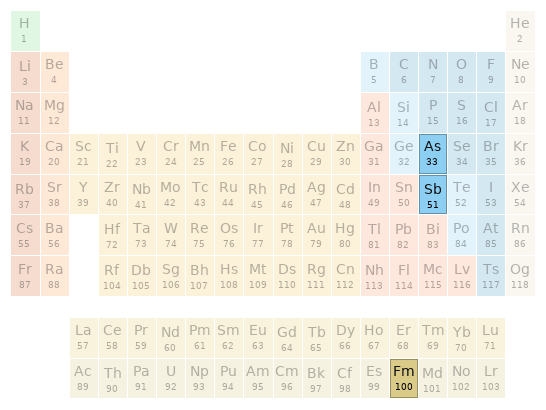
Periodic table location
Images

Images
Basic elemental properties
![| arsenic | antimony | fermium atomic symbol | As | Sb | Fm atomic number | 33 | 51 | 100 short electronic configuration | [Ar]4s^23d^104p^3 | [Kr]5s^24d^105p^3 | [Rn]7s^25f^12 Aufbau diagram | 4p 3d 4s | 5p 4d 5s | 5f 7s block | p | p | f group | 15 | 15 | period | 4 | 5 | 7 atomic mass | 74.921595 u | 121.76 u | 257 u half-life | (stable) | (stable) | 100.5 days](../image_source/3e88510fbd6222320d316a1cfbdf824b.png)
| arsenic | antimony | fermium atomic symbol | As | Sb | Fm atomic number | 33 | 51 | 100 short electronic configuration | [Ar]4s^23d^104p^3 | [Kr]5s^24d^105p^3 | [Rn]7s^25f^12 Aufbau diagram | 4p 3d 4s | 5p 4d 5s | 5f 7s block | p | p | f group | 15 | 15 | period | 4 | 5 | 7 atomic mass | 74.921595 u | 121.76 u | 257 u half-life | (stable) | (stable) | 100.5 days
Thermodynamic properties
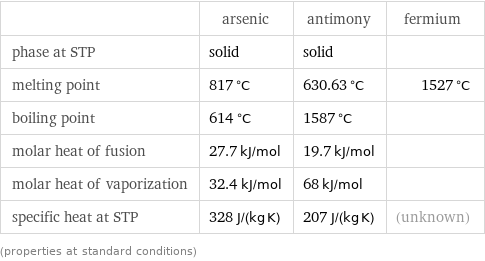
| arsenic | antimony | fermium phase at STP | solid | solid | melting point | 817 °C | 630.63 °C | 1527 °C boiling point | 614 °C | 1587 °C | molar heat of fusion | 27.7 kJ/mol | 19.7 kJ/mol | molar heat of vaporization | 32.4 kJ/mol | 68 kJ/mol | specific heat at STP | 328 J/(kg K) | 207 J/(kg K) | (unknown) (properties at standard conditions)
Material properties
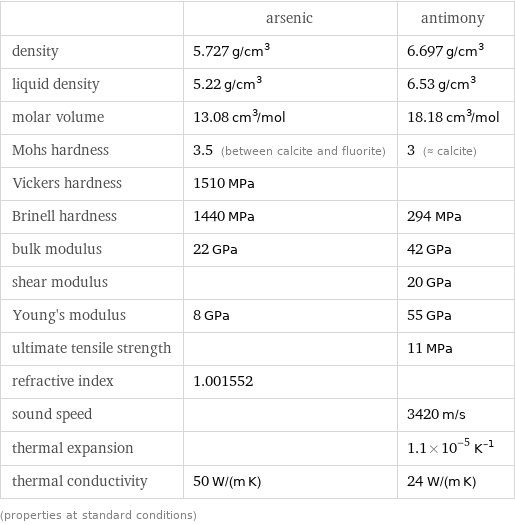
| arsenic | antimony density | 5.727 g/cm^3 | 6.697 g/cm^3 liquid density | 5.22 g/cm^3 | 6.53 g/cm^3 molar volume | 13.08 cm^3/mol | 18.18 cm^3/mol Mohs hardness | 3.5 (between calcite and fluorite) | 3 (≈ calcite) Vickers hardness | 1510 MPa | Brinell hardness | 1440 MPa | 294 MPa bulk modulus | 22 GPa | 42 GPa shear modulus | | 20 GPa Young's modulus | 8 GPa | 55 GPa ultimate tensile strength | | 11 MPa refractive index | 1.001552 | sound speed | | 3420 m/s thermal expansion | | 1.1×10^-5 K^(-1) thermal conductivity | 50 W/(m K) | 24 W/(m K) (properties at standard conditions)
Electromagnetic properties
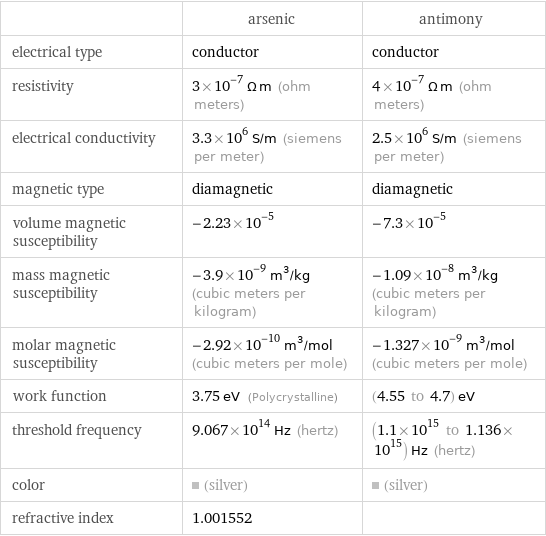
| arsenic | antimony electrical type | conductor | conductor resistivity | 3×10^-7 Ω m (ohm meters) | 4×10^-7 Ω m (ohm meters) electrical conductivity | 3.3×10^6 S/m (siemens per meter) | 2.5×10^6 S/m (siemens per meter) magnetic type | diamagnetic | diamagnetic volume magnetic susceptibility | -2.23×10^-5 | -7.3×10^-5 mass magnetic susceptibility | -3.9×10^-9 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) | -1.09×10^-8 m^3/kg (cubic meters per kilogram) molar magnetic susceptibility | -2.92×10^-10 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) | -1.327×10^-9 m^3/mol (cubic meters per mole) work function | 3.75 eV (Polycrystalline) | (4.55 to 4.7) eV threshold frequency | 9.067×10^14 Hz (hertz) | (1.1×10^15 to 1.136×10^15) Hz (hertz) color | (silver) | (silver) refractive index | 1.001552 |
Reactivity
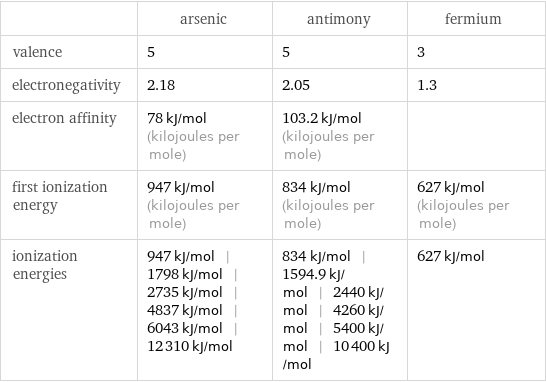
| arsenic | antimony | fermium valence | 5 | 5 | 3 electronegativity | 2.18 | 2.05 | 1.3 electron affinity | 78 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 103.2 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | first ionization energy | 947 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 834 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) | 627 kJ/mol (kilojoules per mole) ionization energies | 947 kJ/mol | 1798 kJ/mol | 2735 kJ/mol | 4837 kJ/mol | 6043 kJ/mol | 12310 kJ/mol | 834 kJ/mol | 1594.9 kJ/mol | 2440 kJ/mol | 4260 kJ/mol | 5400 kJ/mol | 10400 kJ/mol | 627 kJ/mol
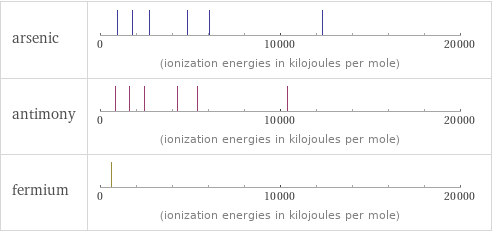
Reactivity
Atomic properties
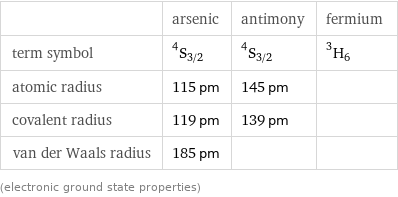
| arsenic | antimony | fermium term symbol | ^4S_(3/2) | ^4S_(3/2) | ^3H_6 atomic radius | 115 pm | 145 pm | covalent radius | 119 pm | 139 pm | van der Waals radius | 185 pm | | (electronic ground state properties)
Abundances
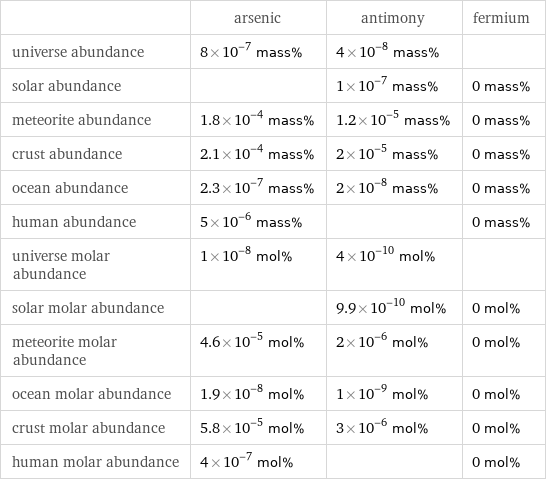
| arsenic | antimony | fermium universe abundance | 8×10^-7 mass% | 4×10^-8 mass% | solar abundance | | 1×10^-7 mass% | 0 mass% meteorite abundance | 1.8×10^-4 mass% | 1.2×10^-5 mass% | 0 mass% crust abundance | 2.1×10^-4 mass% | 2×10^-5 mass% | 0 mass% ocean abundance | 2.3×10^-7 mass% | 2×10^-8 mass% | 0 mass% human abundance | 5×10^-6 mass% | | 0 mass% universe molar abundance | 1×10^-8 mol% | 4×10^-10 mol% | solar molar abundance | | 9.9×10^-10 mol% | 0 mol% meteorite molar abundance | 4.6×10^-5 mol% | 2×10^-6 mol% | 0 mol% ocean molar abundance | 1.9×10^-8 mol% | 1×10^-9 mol% | 0 mol% crust molar abundance | 5.8×10^-5 mol% | 3×10^-6 mol% | 0 mol% human molar abundance | 4×10^-7 mol% | | 0 mol%