Input interpretation
1 M hydrogen (chemical element)
Solution properties
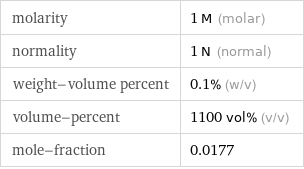
molarity | 1 M (molar) normality | 1 N (normal) weight-volume percent | 0.1% (w/v) volume-percent | 1100 vol% (v/v) mole-fraction | 0.0177
Solute properties per 100 mL
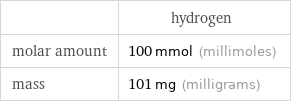
| hydrogen molar amount | 100 mmol (millimoles) mass | 101 mg (milligrams)
Preparation

dilute 1 mol () | hydrogen until 1 L (liter)
Lewis structure

Draw the Lewis structure of hydrogen. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule: Count the total valence electrons of the hydrogen (n_H, val = 1) atoms: 2 n_H, val = 2 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for hydrogen (n_H, full = 2): 2 n_H, full = 4 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 4 - 2 = 2 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. There is 1 bond and hence 2 bonding electrons in the diagram. Lastly, fill in the remaining unbonded electrons on each atom. In total, there remain 2 - 2 = 0 electrons left to draw and the diagram is complete: Answer: | |
Chemical names and formulas
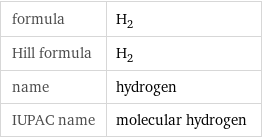
formula | H_2 Hill formula | H_2 name | hydrogen IUPAC name | molecular hydrogen
Substance properties
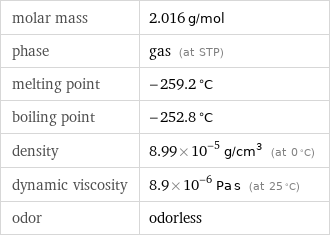
molar mass | 2.016 g/mol phase | gas (at STP) melting point | -259.2 °C boiling point | -252.8 °C density | 8.99×10^-5 g/cm^3 (at 0 °C) dynamic viscosity | 8.9×10^-6 Pa s (at 25 °C) odor | odorless
Units
