Input interpretation
period 6 elements | superconducting point
Summary

median | 1.7 K highest | 7.2 K (lead) lowest | 0.015 K (tungsten) distribution | | (based on 13 values; 19 unavailable)
Entities with missing values
cesium | barium | praseodymium | neodymium | promethium | samarium | gadolinium | terbium | dysprosium | holmium | ... (total: 19)
Distribution plots
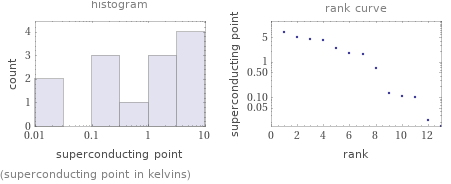
(superconducting point in kelvins)
Superconducting point rankings
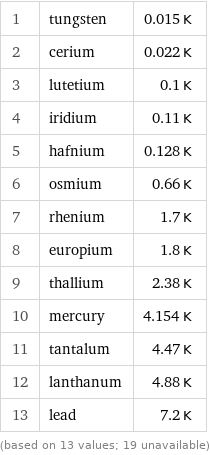
1 | tungsten | 0.015 K 2 | cerium | 0.022 K 3 | lutetium | 0.1 K 4 | iridium | 0.11 K 5 | hafnium | 0.128 K 6 | osmium | 0.66 K 7 | rhenium | 1.7 K 8 | europium | 1.8 K 9 | thallium | 2.38 K 10 | mercury | 4.154 K 11 | tantalum | 4.47 K 12 | lanthanum | 4.88 K 13 | lead | 7.2 K (based on 13 values; 19 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median superconducting point 1.7 K

-271.45 °C (degrees Celsius)
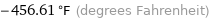
-456.61 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)

3.06 °R (degrees Rankine)

-217.16 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)

-135.01 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median superconducting point 1.7 K

0.7 K above temperature of coldest known natural environment (Boomerang nebula) (1 K)
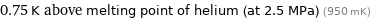
0.75 K above melting point of helium (at 2.5 MPa) (950 mK)
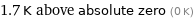
1.7 K above absolute zero (0 K)
Corresponding quantity
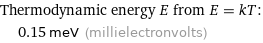
Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 0.15 meV (millielectronvolts)