Input interpretation
Bell Coleman cycle
Equation
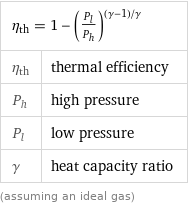
η_th = 1 - (P_l/P_h)^((γ - 1)/γ) | η_th | thermal efficiency P_h | high pressure P_l | low pressure γ | heat capacity ratio (assuming an ideal gas)
Input values
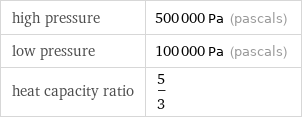
high pressure | 500000 Pa (pascals) low pressure | 100000 Pa (pascals) heat capacity ratio | 5/3
Results

thermal efficiency | 0.4747 = 47.47%
Possible intermediate steps

Calculate the thermal efficiency using the following information: known variables | | P_h | high pressure | 500000 Pa P_l | low pressure | 100000 Pa γ | heat capacity ratio | 5/3 Convert known variables into appropriate units using the following: 1 Pa = 1000 g/(m s^2): 1 Pa = 1000 g/(m s^2): known variables | | P_h | high pressure | 5×10^8 g/(m s^2) P_l | low pressure | 1×10^8 g/(m s^2) γ | heat capacity ratio | 5/3 The relevant equation that relates thermal efficiency (η_th), high pressure (P_h), low pressure (P_l), and heat capacity ratio (γ) is: η_th = 1 - (P_l/P_h)^((γ - 1)/γ) Substitute known variables into the equation: known variables | | P_h | high pressure | 5×10^8 g/(m s^2) P_l | low pressure | 1×10^8 g/(m s^2) γ | heat capacity ratio | 5/3 | : η_th = 1 - ((1×10^8 g/(m s^2))/(5×10^8 g/(m s^2)))^((5/3 - 1)/5/3) Cancel the units in 1 - ((1×10^8 g/(m s^2))/(5×10^8 g/(m s^2)))^((5/3 - 1)/5/3): η_th = 1 - ((1×10^8)/(5×10^8))^((5/3 - 1)/5/3) Evaluate 1 - ((1×10^8)/(5×10^8))^((5/3 - 1)/5/3): Answer: | | η_th = 0.4747
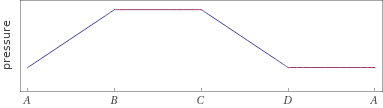
Pressure vs. volume
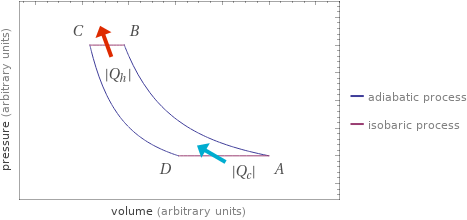
Pressure vs. volume
Temperature vs. entropy
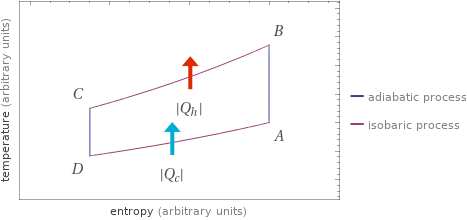
Temperature vs. entropy
Possible time evolution
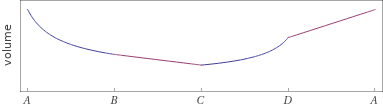
Possible time evolution
Possible time evolution
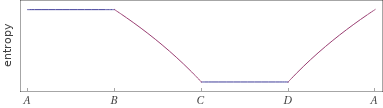
Possible time evolution
Possible time evolution