Input interpretation
sulfuric acid
Chemical names and formulas

formula | H_2SO_4 Hill formula | H_2O_4S name | sulfuric acid alternate names | anhydrous sulfuric acid | dihydrogen sulfate | oil of vitriol | sulphuric acid mass fractions | H (hydrogen) 2.06% | O (oxygen) 65.3% | S (sulfur) 32.7%
Lewis structure
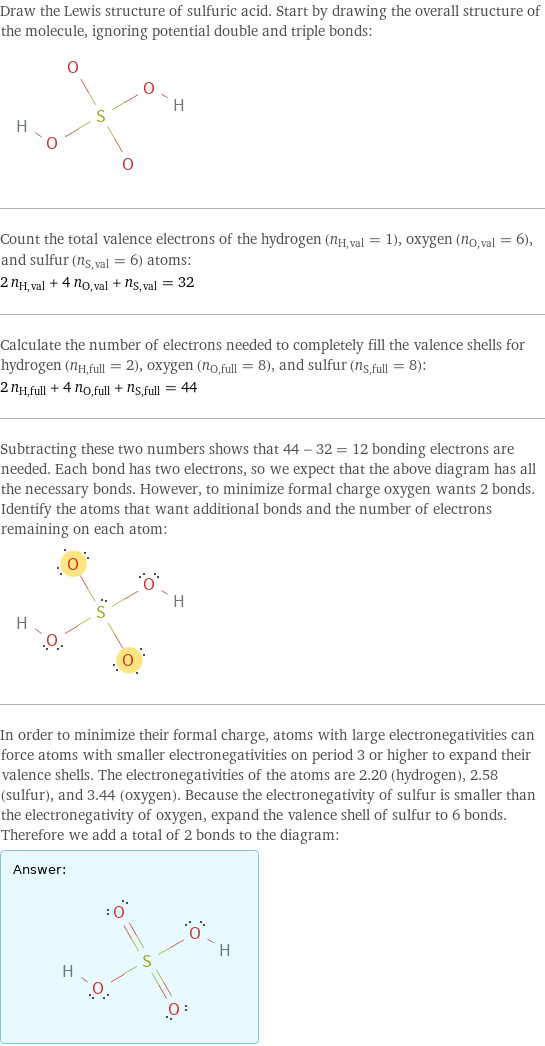
Draw the Lewis structure of sulfuric acid. Start by drawing the overall structure of the molecule, ignoring potential double and triple bonds: Count the total valence electrons of the hydrogen (n_H, val = 1), oxygen (n_O, val = 6), and sulfur (n_S, val = 6) atoms: 2 n_H, val + 4 n_O, val + n_S, val = 32 Calculate the number of electrons needed to completely fill the valence shells for hydrogen (n_H, full = 2), oxygen (n_O, full = 8), and sulfur (n_S, full = 8): 2 n_H, full + 4 n_O, full + n_S, full = 44 Subtracting these two numbers shows that 44 - 32 = 12 bonding electrons are needed. Each bond has two electrons, so we expect that the above diagram has all the necessary bonds. However, to minimize formal charge oxygen wants 2 bonds. Identify the atoms that want additional bonds and the number of electrons remaining on each atom: In order to minimize their formal charge, atoms with large electronegativities can force atoms with smaller electronegativities on period 3 or higher to expand their valence shells. The electronegativities of the atoms are 2.20 (hydrogen), 2.58 (sulfur), and 3.44 (oxygen). Because the electronegativity of sulfur is smaller than the electronegativity of oxygen, expand the valence shell of sulfur to 6 bonds. Therefore we add a total of 2 bonds to the diagram: Answer: | |
3D structure
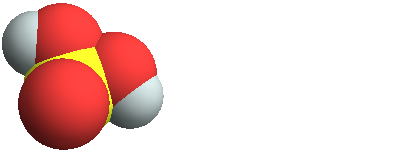
3D structure
Basic properties
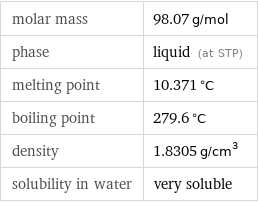
molar mass | 98.07 g/mol phase | liquid (at STP) melting point | 10.371 °C boiling point | 279.6 °C density | 1.8305 g/cm^3 solubility in water | very soluble
Units

Liquid properties (at STP)
density | 1.8305 g/cm^3 vapor pressure | 6×10^-5 mmHg dynamic viscosity | 0.021 Pa s (at 25 °C) surface tension | 0.0735 N/m refractive index | 1.41827
Units
Thermodynamic properties
specific heat capacity c_p | liquid | 1.416 J/(g K) molar heat capacity c_p | liquid | 138.9 J/(mol K) specific free energy of formation Δ_fG° | liquid | -7.036 kJ/g molar free energy of formation Δ_fG° | liquid | -690 kJ/mol specific heat of formation Δ_fH° | aqueous | -9.269 kJ/g | liquid | -8.3 kJ/g molar heat of formation Δ_fH° | aqueous | -909 kJ/mol | liquid | -814 kJ/mol specific entropy S° | aqueous | 0.2039 J/(g K) | liquid | 1.601 J/(g K) molar entropy S° | aqueous | 20 J/(mol K) | liquid | 157 J/(mol K) molar heat of vaporization | 56 kJ/mol | specific heat of vaporization | 0.57 kJ/g | molar heat of fusion | 10.71 kJ/mol | specific heat of fusion | 0.1092 kJ/g | (at STP)
Chemical identifiers
CAS number | 7664-93-9 Beilstein number | 2037554 PubChem CID number | 1118 PubChem SID number | 24859176 SMILES identifier | OS(=O)(=O)O InChI identifier | InChI=1/H2O4S/c1-5(2, 3)4/h(H2, 1, 2, 3, 4)/f/h1-2H MDL number | MFCD00064589
NFPA label

NFPA label
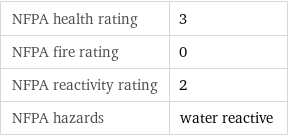
NFPA health rating | 3 NFPA fire rating | 0 NFPA reactivity rating | 2 NFPA hazards | water reactive
Toxicity properties

odor | odorless threshold limit value | 0.05 ppmv
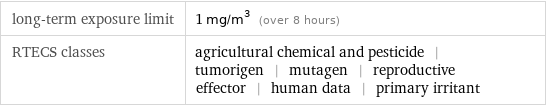
long-term exposure limit | 1 mg/m^3 (over 8 hours) RTECS classes | agricultural chemical and pesticide | tumorigen | mutagen | reproductive effector | human data | primary irritant
Ion equivalents

H^+ (hydrogen cation) | 2 (SO_4)^(2-) (sulfate anion) | 1