Input interpretation

vitamins | molar mass
Summary

median | 300.8 g/mol highest | 430.72 g/mol (α-tocopherol and D-alpha-tocopherol) lowest | 123.11 g/mol (niacin) distribution |
Units

Distribution plots
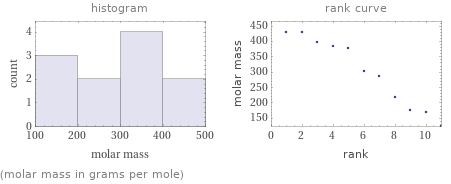
(molar mass in grams per mole)
Molar mass rankings
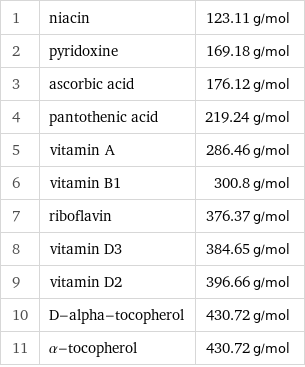
1 | niacin | 123.11 g/mol 2 | pyridoxine | 169.18 g/mol 3 | ascorbic acid | 176.12 g/mol 4 | pantothenic acid | 219.24 g/mol 5 | vitamin A | 286.46 g/mol 6 | vitamin B1 | 300.8 g/mol 7 | riboflavin | 376.37 g/mol 8 | vitamin D3 | 384.65 g/mol 9 | vitamin D2 | 396.66 g/mol 10 | D-alpha-tocopherol | 430.72 g/mol 11 | α-tocopherol | 430.72 g/mol
Unit conversion for median molar mass 300.8 g/mol
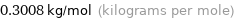
0.3008 kg/mol (kilograms per mole)
Comparisons for median molar mass 300.8 g/mol
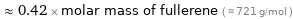
≈ 0.42 × molar mass of fullerene ( ≈ 721 g/mol )
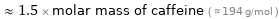
≈ 1.5 × molar mass of caffeine ( ≈ 194 g/mol )
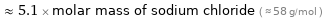
≈ 5.1 × molar mass of sodium chloride ( ≈ 58 g/mol )
Corresponding quantities
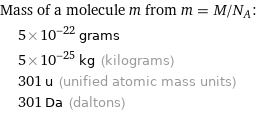
Mass of a molecule m from m = M/N_A: | 5×10^-22 grams | 5×10^-25 kg (kilograms) | 301 u (unified atomic mass units) | 301 Da (daltons)
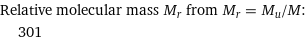
Relative molecular mass M_r from M_r = M_u/M: | 301