Input interpretation
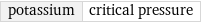
potassium | critical pressure
Result
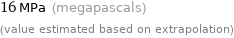
16 MPa (megapascals) (value estimated based on extrapolation)
Unit conversions
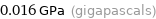
0.016 GPa (gigapascals)
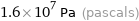
1.6×10^7 Pa (pascals)

1.6×10^7 N/m^2 (newtons per square meter)
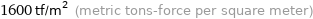
1600 tf/m^2 (metric tons-force per square meter)
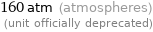
160 atm (atmospheres) (unit officially deprecated)
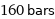
160 bars
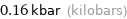
0.16 kbar (kilobars)

1.6 km WC (kilometers of water column)
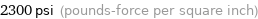
2300 psi (pounds-force per square inch)
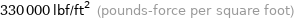
330000 lbf/ft^2 (pounds-force per square foot)
Comparisons as pressure
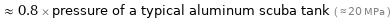
≈ 0.8 × pressure of a typical aluminum scuba tank ( ≈ 20 MPa )
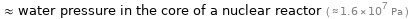
≈ water pressure in the core of a nuclear reactor ( ≈ 1.6×10^7 Pa )
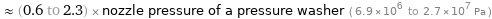
≈ (0.6 to 2.3) × nozzle pressure of a pressure washer ( 6.9×10^6 to 2.7×10^7 Pa )
Corresponding quantity
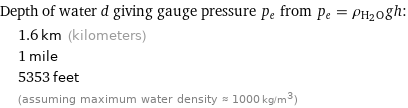
Depth of water d giving gauge pressure p_e from p_e = ρ_(H_2O)gh: | 1.6 km (kilometers) | 1 mile | 5353 feet | (assuming maximum water density ≈ 1000 kg/m^3)