Input interpretation

NOx compounds | boiling point
Results

nitric oxide | -151.7 °C (degrees Celsius) nitrogen dioxide | 21 °C (degrees Celsius)

NOx compounds | boiling point | -65.35 °C (degrees Celsius) (median)
Unit conversions for median boiling point -65.35 °C
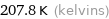
207.8 K (kelvins)

-85.63 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)

374 °R (degrees Rankine)
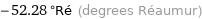
-52.28 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)

-26.81 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median boiling point -65.35 °C
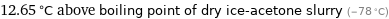
12.65 °C above boiling point of dry ice-acetone slurry (-78 °C)
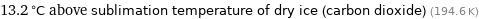
13.2 °C above sublimation temperature of dry ice (carbon dioxide) (194.6 K)
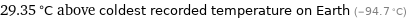
29.35 °C above coldest recorded temperature on Earth (-94.7 °C)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 18 meV (millielectronvolts)
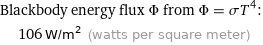
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 106 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 7.9×10^-34 lx (lux)