Input interpretation
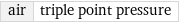
air | triple point pressure
Result
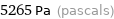
5265 Pa (pascals)
Unit conversions
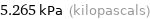
5.265 kPa (kilopascals)

5265 N/m^2 (newtons per square meter)
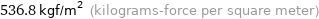
536.8 kgf/m^2 (kilograms-force per square meter)
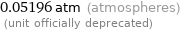
0.05196 atm (atmospheres) (unit officially deprecated)

0.05368 at (technical atmospheres) (unit officially deprecated)
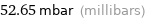
52.65 mbar (millibars)
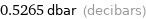
0.5265 dbar (decibars)
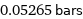
0.05265 bars
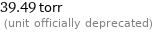
39.49 torr (unit officially deprecated)
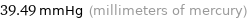
39.49 mmHg (millimeters of mercury)
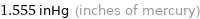
1.555 inHg (inches of mercury)

53.68 cm WC (centimeters of water column)

536.8 mm WC (millimeters of water column)

0.5368 m WC (meters of water column)

21.14 in WC (inches of water column (conventional))

0.7636 psi (pounds-force per square inch)

110 lbf/ft^2 (pounds-force per square foot)
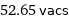
52.65 vacs
Comparisons as pressure
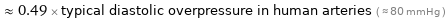
≈ 0.49 × typical diastolic overpressure in human arteries ( ≈ 80 mmHg )
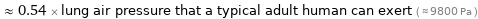
≈ 0.54 × lung air pressure that a typical adult human can exert ( ≈ 9800 Pa )
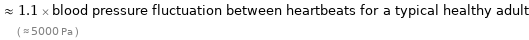
≈ 1.1 × blood pressure fluctuation between heartbeats for a typical healthy adult ( ≈ 5000 Pa )
Corresponding quantities
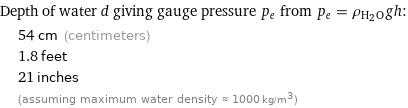
Depth of water d giving gauge pressure p_e from p_e = ρ_(H_2O)gh: | 54 cm (centimeters) | 1.8 feet | 21 inches | (assuming maximum water density ≈ 1000 kg/m^3)

Standard Atmosphere altitude: | 20 km (kilometers) | 13 miles | (based on 1976 US Standard Atmosphere)
Triple point
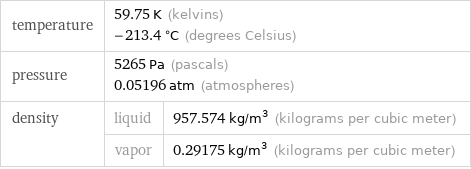
temperature | 59.75 K (kelvins) -213.4 °C (degrees Celsius) | pressure | 5265 Pa (pascals) 0.05196 atm (atmospheres) | density | liquid | 957.574 kg/m^3 (kilograms per cubic meter) | vapor | 0.29175 kg/m^3 (kilograms per cubic meter)
Phase diagram
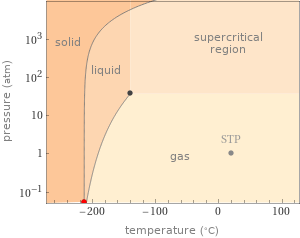
Phase diagram