Input interpretation
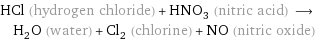
HCl (hydrogen chloride) + HNO_3 (nitric acid) ⟶ H_2O (water) + Cl_2 (chlorine) + NO (nitric oxide)
Balanced equation

Balance the chemical equation algebraically: HCl + HNO_3 ⟶ H_2O + Cl_2 + NO Add stoichiometric coefficients, c_i, to the reactants and products: c_1 HCl + c_2 HNO_3 ⟶ c_3 H_2O + c_4 Cl_2 + c_5 NO Set the number of atoms in the reactants equal to the number of atoms in the products for Cl, H, N and O: Cl: | c_1 = 2 c_4 H: | c_1 + c_2 = 2 c_3 N: | c_2 = c_5 O: | 3 c_2 = c_3 + c_5 Since the coefficients are relative quantities and underdetermined, choose a coefficient to set arbitrarily. To keep the coefficients small, the arbitrary value is ordinarily one. For instance, set c_2 = 1 and solve the system of equations for the remaining coefficients: c_1 = 3 c_2 = 1 c_3 = 2 c_4 = 3/2 c_5 = 1 Multiply by the least common denominator, 2, to eliminate fractional coefficients: c_1 = 6 c_2 = 2 c_3 = 4 c_4 = 3 c_5 = 2 Substitute the coefficients into the chemical reaction to obtain the balanced equation: Answer: | | 6 HCl + 2 HNO_3 ⟶ 4 H_2O + 3 Cl_2 + 2 NO
Structures
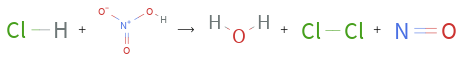
+ ⟶ + +
Names
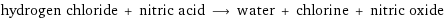
hydrogen chloride + nitric acid ⟶ water + chlorine + nitric oxide
Reaction thermodynamics
Gibbs free energy
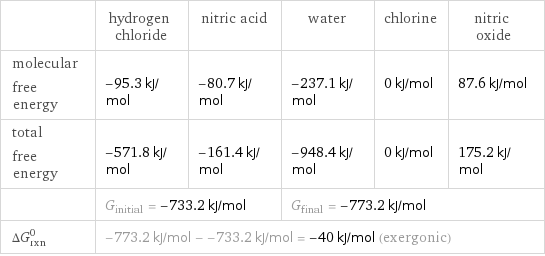
| hydrogen chloride | nitric acid | water | chlorine | nitric oxide molecular free energy | -95.3 kJ/mol | -80.7 kJ/mol | -237.1 kJ/mol | 0 kJ/mol | 87.6 kJ/mol total free energy | -571.8 kJ/mol | -161.4 kJ/mol | -948.4 kJ/mol | 0 kJ/mol | 175.2 kJ/mol | G_initial = -733.2 kJ/mol | | G_final = -773.2 kJ/mol | | ΔG_rxn^0 | -773.2 kJ/mol - -733.2 kJ/mol = -40 kJ/mol (exergonic) | | | |
Entropy
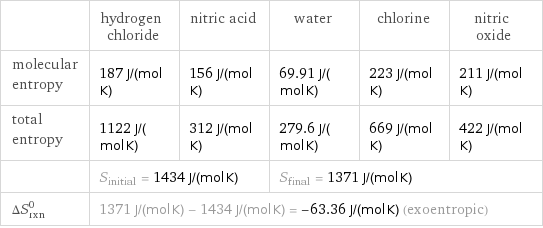
| hydrogen chloride | nitric acid | water | chlorine | nitric oxide molecular entropy | 187 J/(mol K) | 156 J/(mol K) | 69.91 J/(mol K) | 223 J/(mol K) | 211 J/(mol K) total entropy | 1122 J/(mol K) | 312 J/(mol K) | 279.6 J/(mol K) | 669 J/(mol K) | 422 J/(mol K) | S_initial = 1434 J/(mol K) | | S_final = 1371 J/(mol K) | | ΔS_rxn^0 | 1371 J/(mol K) - 1434 J/(mol K) = -63.36 J/(mol K) (exoentropic) | | | |
Equilibrium constant
![K_c = ([H2O]^4 [Cl2]^3 [NO]^2)/([HCl]^6 [HNO3]^2)](../image_source/e5cab438602942eb6785e06de5dee90e.png)
K_c = ([H2O]^4 [Cl2]^3 [NO]^2)/([HCl]^6 [HNO3]^2)
Rate of reaction
![rate = -1/6 (Δ[HCl])/(Δt) = -1/2 (Δ[HNO3])/(Δt) = 1/4 (Δ[H2O])/(Δt) = 1/3 (Δ[Cl2])/(Δt) = 1/2 (Δ[NO])/(Δt) (assuming constant volume and no accumulation of intermediates or side products)](../image_source/8bb982d348be219793e68cee7bda0243.png)
rate = -1/6 (Δ[HCl])/(Δt) = -1/2 (Δ[HNO3])/(Δt) = 1/4 (Δ[H2O])/(Δt) = 1/3 (Δ[Cl2])/(Δt) = 1/2 (Δ[NO])/(Δt) (assuming constant volume and no accumulation of intermediates or side products)
Chemical names and formulas
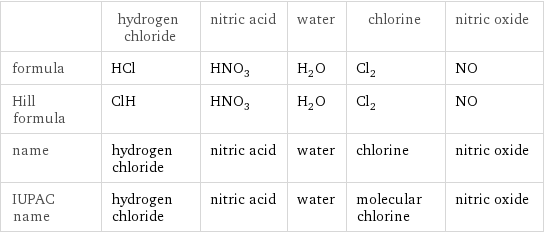
| hydrogen chloride | nitric acid | water | chlorine | nitric oxide formula | HCl | HNO_3 | H_2O | Cl_2 | NO Hill formula | ClH | HNO_3 | H_2O | Cl_2 | NO name | hydrogen chloride | nitric acid | water | chlorine | nitric oxide IUPAC name | hydrogen chloride | nitric acid | water | molecular chlorine | nitric oxide