Input interpretation
strong acids | boiling point
Summary
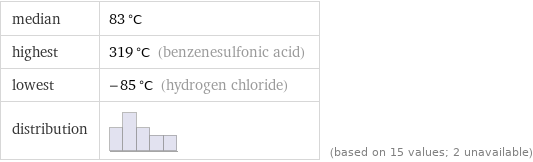
median | 83 °C highest | 319 °C (benzenesulfonic acid) lowest | -85 °C (hydrogen chloride) distribution | | (based on 15 values; 2 unavailable)
Entities with missing values
chromic acid | iodic acid (total: 2)
Distribution plots
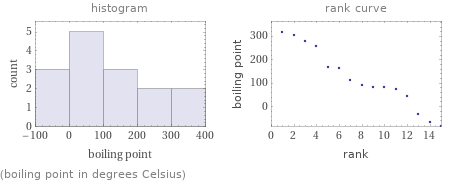
(boiling point in degrees Celsius)
Boiling point rankings
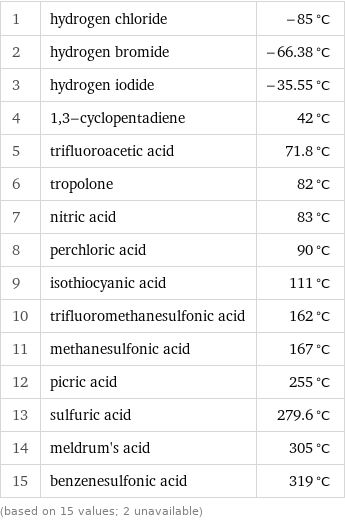
1 | hydrogen chloride | -85 °C 2 | hydrogen bromide | -66.38 °C 3 | hydrogen iodide | -35.55 °C 4 | 1, 3-cyclopentadiene | 42 °C 5 | trifluoroacetic acid | 71.8 °C 6 | tropolone | 82 °C 7 | nitric acid | 83 °C 8 | perchloric acid | 90 °C 9 | isothiocyanic acid | 111 °C 10 | trifluoromethanesulfonic acid | 162 °C 11 | methanesulfonic acid | 167 °C 12 | picric acid | 255 °C 13 | sulfuric acid | 279.6 °C 14 | meldrum's acid | 305 °C 15 | benzenesulfonic acid | 319 °C (based on 15 values; 2 unavailable)
Unit conversions for median boiling point 83 °C
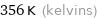
356 K (kelvins)
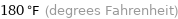
180 °F (degrees Fahrenheit)

640 °R (degrees Rankine)

66 °Ré (degrees Réaumur)
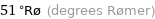
51 °Rø (degrees Rømer)
Comparison for median boiling point 83 °C
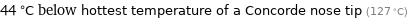
44 °C below hottest temperature of a Concorde nose tip (127 °C)
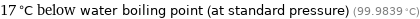
17 °C below water boiling point (at standard pressure) (99.9839 °C)
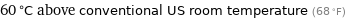
60 °C above conventional US room temperature (68 °F)
Corresponding quantities

Thermodynamic energy E from E = kT: | 31 meV (millielectronvolts)
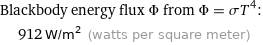
Blackbody energy flux Φ from Φ = σT^4: | 912 W/m^2 (watts per square meter)

Approximate luminous exitance from a planar blackbody radiator perpendicular to its surface: | 6.7×10^-17 lx (lux)
Nearest corresponding gas marks for median boiling point 83 °C (degrees Celsius)

| temperature | usage thermostat 3 | 90 °C | France (actual measurements may vary)